glkA is involved in glucose repression of chitinase production in Streptomyces lividans
- PMID: 9603881
- PMCID: PMC107258
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.11.2911-2914.1998
glkA is involved in glucose repression of chitinase production in Streptomyces lividans
Abstract
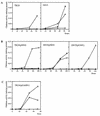
Chitinase production in Streptomyces lividans is induced by chitin and repressed in the presence of glucose. A mutant of S. lividans TK24, strain G015, which was defective in glucose repression of chitinase production, was obtained by screening colonies for zones of clearing on colloidal chitin agar plates containing 1.0% (wt/vol) glucose. The transcriptional analysis of chiA in G015 with xylE, which encodes catechol 2,3-dioxygenase, as a reporter gene showed that the transcription from the chiA promoter of S. lividans TK24 occurred regardless of the presence of glucose. G015 was resistant to 2-deoxyglucose (2-DOG) and did not utilize glucose as a sole carbon source. When a DNA fragment containing glkA, a gene for glucose kinase, of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) was introduced into strain G015 on a low-copy-number plasmid, the sensitivity to 2-DOG, the ability to utilize glucose, and the glucose repression of chitinase production were restored. These results indicate that glkA is involved in glucose repression of chitinase production in S. lividans TK24.
Figures
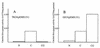
References
-
- Angell S, Lewis C G, Buttner M J, Bibb M J. Glucose repression in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): a likely regulatory role for glucose kinase. Mol Gen Genet. 1994;244:135–143. - PubMed
-
- Angell S, Schwarz E, Bibb M J. The glucose kinase gene of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): its nucleotide sequence, transcriptional analysis and role in glucose repression. Mol Microbiol. 1992;6:2833–2844. - PubMed
-
- Blaak H, Schnellmann J, Walter S, Henrissat B, Schrempf H. Characteristics of an exochitinase from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis, its corresponding gene, putative protein domains and relationship to other chitinases. Eur J Biochem. 1993;214:659–669. - PubMed
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

