Effect of cytokines on anticryptococcal activity of human microglial cells
- PMID: 9606001
- PMCID: PMC104534
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.5.3.410-411.1998
Effect of cytokines on anticryptococcal activity of human microglial cells
Abstract
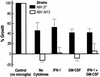
The effect of selected cytokines on the antifungal activity of human microglia was studied with encapsulated and acapsular strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. None of the cytokines tested increased the fungistatic activity of microglia, suggesting that killing of cryptococci within the central nervous system is dependent on other host defense mechanisms.
Figures
References
-
- Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Mazolla R, Tancini B, Saleppico S, Puliti M, Pitzurra L, Bistoni F. Role of nitric oxide and melanogenesis in the accomplishment of anticryptococcal activity by the BV-2 microglial cell line. J Neuroimmunol. 1995;58:111–116. - PubMed
-
- Chao C C, Hu S, Gekker G, Novick W J, Jr, Remingotn J S, Peterson P K. Effects of cytokines on multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii in microglial cells. J Immunol. 1993;150:3404–3410. - PubMed
-
- Chao C C, Anderson W R, Hu S, Martella A, Gekker G, Peterson P K. Activated microglia inhibit Toxoplasma gondii via a nitric oxide mechanism. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1993;67:178–183. - PubMed
-
- Chao C C, Gekker G, Hu S, Peterson P K. Human microglial cell defense against Toxoplasma gondii. The role of cytokines. J Immunol. 1994;152:1246–1252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

