Differential subcellular localization of protein phosphatase-1 alpha, gamma1, and delta isoforms during both interphase and mitosis in mammalian cells
- PMID: 9606212
- PMCID: PMC2137188
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.5.1207
Differential subcellular localization of protein phosphatase-1 alpha, gamma1, and delta isoforms during both interphase and mitosis in mammalian cells
Abstract
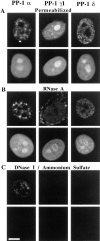
Protein phosphatase-1 (PP-1) is involved in the regulation of numerous metabolic processes in mammalian cells. The major isoforms of PP-1, alpha, gamma1, and delta, have nearly identical catalytic domains, but they vary in sequence at their extreme NH2 and COOH termini. With specific antibodies raised against the unique COOH-terminal sequence of each isoform, we find that the three PP-1 isoforms are each expressed in all mammalian cells tested, but that they localize within these cells in a strikingly distinct and characteristic manner. Each isoform is present both within the cytoplasm and in the nucleus during interphase. Within the nucleus, PP-1 alpha associates with the nuclear matrix, PP-1 gamma1 concentrates in nucleoli in association with RNA, and PP-1 delta localizes to nonnucleolar whole chromatin. During mitosis, PP-1 alpha is localized to the centrosome, PP-1 gamma1 is associated with microtubules of the mitotic spindle, and PP-1 delta strongly associates with chromosomes. We conclude that PP-1 isoforms are targeted to strikingly distinct and independent sites in the cell, permitting unique and independent roles for each of the isoforms in regulating discrete cellular processes.
Figures





References
-
- Alessi DR, Street AJ, Cohen P, Cohen PTW. Inhibitor-2 functions like a chaperone to fold three expressed isoforms of mammalian protein phosphatase-1 into a conformation with the specificity and regulatory properties of the native enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1993;213:1055–1066. - PubMed
-
- Axton JM, Dombradi V, Cohen PTW, Glover DM. One of the protein phosphatase 1 isoenzymes in Drosophila is essential for mitosis. Cell. 1990;63:33–46. - PubMed
-
- Barker HM, Craig SP, Spurr NK, Cohen PTW. Sequence of human protein serine/threonine phosphatase 1 γ and localization of the gene (PPP1CC) encoding it to chromosome bands 12q24.1-q24.2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993;1178:228–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

