Immune responses in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV)
- PMID: 9613472
- PMCID: PMC7119871
- DOI: 10.1016/s0165-2427(97)00134-7
Immune responses in pigs infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV)
Abstract
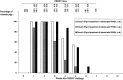
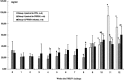
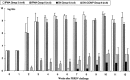
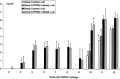
In three successive experiments, the immune functions of pigs persistently infected with the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) have been evaluated. Non-specific immune responses were analyzed over a period of 12 weeks post-infection (PI). In addition, the capacity of PRRSV-infected pigs to develop an efficient immune response against pseudorabies virus (PRV) glycoproteins and to resist to a subsequent virulent challenge was investigated. Our results demonstrate that PRRSV produced minor effects on the immune system of pigs. The skin delayed type hypersensitivity (DTH) in response to phytohemagglutinine injection was slightly diminished one week after challenge, but was restored thereafter. However, three weeks after the infection, the total white blood cell count, and the number of CD2+, CD8+ and IgM+ cells were enhanced. The increase in numbers of CD8+ cells persisted for three consecutive weeks. Serum immunoglobulins in infected pigs also increased by week 3 PI and up to 8 weeks PI. These results show that PRRSV may have stimulating effects on the pig immune system during the phase of long-lasting infection. After immunization with PRV glycoproteins, the production of anti-PRV antibodies and skin DTH response against PRV glycoproteins were not affected. On the contrary, following a virulent PRV challenge, PRRSV-infected pigs developed a better secondary antibody response and their resistance to the infection was as effective as in control pigs. Taken together, our data do not support a systemic immunosuppressive effect of PRRSV, during the persistent phase of infection. Other mechanisms may therefore apply to explain the emergence of secondary infections in endemically infected herds.
Figures

References
-
- Albina E, Madec F, Cariolet R, Torrison J. Immune response and persistence of the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in infected pigs and farm units. Vet. Rec. 1994;134:567–573. - PubMed
-
- Albina E, Kobisch M, Cariolet R, Morvan P, Keranflec'h A, Beaurepaire B, Hutet E, Labbé A. Le syndrome dysgénésique et respiratoire du porc (SDRP): étude expérimentale des effets de l'infection sur la réponse immunitaire et la résistance aux infections Aujeszky et Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae chez le porc en croissance. Journées Rech Porcine en France. 1995;27:107–116.
-
- Andries K, Pensaert M.B, Vandeputte J. Effect of experimental infection with pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus on pigs with maternal immunity from vaccinated sows. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978;39:1282–1285. - PubMed
-
- Baron T, Albina E, Leforban Y, Madec F, Guilmoto H, Plana Duran J, Vannier P. Report on the first outbreak of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) in France: diagnosis and viral isolation. Ann. Rech. Vet. 1992;23:161–166. - PubMed
-
- Bautista, E.M., Meulenberg, J.M.M., Choi, C.S., Pol, J., Molitor, T.W., 1996. PRRSV-specific responses in infected and vaccinated pigs. Proceedings of 14th International Pig Veterinary Society Congress, Bologna, Italy, 7–10 July, 63.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

