Odorant response properties of convergent olfactory receptor neurons
- PMID: 9614232
- PMCID: PMC6792685
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-12-04560.1998
Odorant response properties of convergent olfactory receptor neurons
Abstract
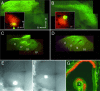
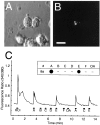
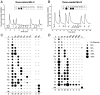
Information about odorant stimuli is thought to be represented in spatial and temporal patterns of activity across neurons in the olfactory epithelium and the olfactory bulb (OB). Previous studies suggest that olfactory receptor neurons (ORNs) distributed in the nasal cavity project to localized regions in the glomerular layer of the OB. However, the functional significance of this convergence is not yet known, and in no studies have the odorant response properties of individual ORNs projecting to defined OB regions been measured directly. We have retrogradely labeled mouse ORNs connecting to different glomeruli in the dorsal OB and tested single cells for responses to odorants using fura-2 calcium imaging. ORNs that project to clusters of dorsomedial (DM) glomeruli exhibit different odorant response profiles from those that project to dorsolateral (DL) glomeruli. DL-projecting ORNs showed responses to compounds with widely different structures, including carvone, eugenol, cinnamaldehyde, and acetophenone. In contrast, DM-projecting neurons exhibited responses to a more structurally restricted set of compounds and responded preferentially to organic acids. These data demonstrate that ORN afferents segregate by odorant responsiveness and that the homogeneity of ORN and glomerular input varies with different OB regions. The data also demonstrate that a subpopulation of ORNs projecting to DM glomeruli is functionally similar.
Figures

References
-
- Astic L, Saucier D. Anatomical mapping of the neuroepithelial projection to the olfactory bulb in the rat. Brain Res Bull. 1986;16:445–454. - PubMed
-
- Astic L, Saucier D, Holley A. Topographical relationships between olfactory receptor cells and glomerular foci in the rat olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 1987;424:144–152. - PubMed
-
- Bell GA, Laing DG, Panhuber H. Odor mixture suppression: evidence for a peripheral mechanism in human and rat. Brain Res. 1987;426:8–18. - PubMed
-
- Breer H, Boekhoff I. Odorants of the same odor class activate different second messenger pathways. Chem Senses. 1991;16:19–29.
-
- Cinelli AR, Hamilton KA, Kauer JS. Salamander olfactory bulb neuronal activity observed by video rate, voltage-sensitive dye imaging: III. Spatial and temporal properties of responses evoked by odorant stimulation. J Neurophysiol. 1995;73:2053–2071. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
