Electrophysiological development of central neurons in the Drosophila embryo
- PMID: 9614242
- PMCID: PMC6792699
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-12-04673.1998
Electrophysiological development of central neurons in the Drosophila embryo
Abstract
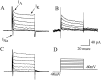
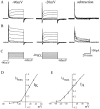
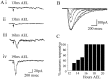
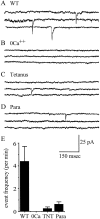
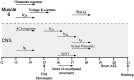
In this study, we describe the development of electrical properties of Drosophila embryonic central neurons in vivo. Using whole-cell voltage clamp, we describe the onset of expression of specific voltage- and ligand-gated ionic currents and the first appearance of endogenous and synaptic activity. The first currents occur during midembryogenesis [late stage 16, 13-14 hr after egg laying (AEL)] and consist of a delayed outward potassium current (IK) and an acetylcholine-gated inward cation current (IACh). As development proceeds, other voltage-activated currents arise sequentially. An inward calcium current (ICa) is first observed at 15 hr AEL, an inward sodium current (INa) at 16 hr AEL, and a rapidly inactivating outward potassium current (IA) at 17 hr AEL. The inward calcium current is composed of at least two individual and separable components that exhibit small temporal differences in their development. Endogenous activity is first apparent at 15 hr AEL and consists of small events (peak amplitude, 5 pA) that probably result from the random opening of relatively few numbers of ion channels. At 16 hr AEL, discrete (10-15 msec duration) currents that exhibit larger amplitude (25 pA maximum) and rapid activation but slower inactivation first appear. We identify these latter currents as EPSCs, an indication that functional synaptic transmission is occurring. In the neurons from which we record, action potentials first occur at 17 hr AEL. This study is the first to record from Drosophila embryonic central neurons in vivo and makes possible future work to define the factors that shape the electrical properties of neurons during development.
Figures





References
-
- Aisemberg GO, Gershon TR, Macagno ER. New electrical properties of neurons induced by a homeoprotein. J Neurobiol. 1997;33:11–17. - PubMed
-
- Baines RA, Bacon JP. Pharmacological analysis of the cholinergic input to the locust VPLI neuron from an extraocular photoreceptor system. J Neurophysiol. 1994;72:2864–2874. - PubMed
-
- Baker K, Salkoff L. The Drosophila shaker gene codes for a distinctive K+ current in a subset of neurons. Neuron. 1990;2:129–140. - PubMed
-
- Benson JA. Electrophysiological pharmacology of the nicotinic and muscarinic cholinergic responses of isolated neuronal somata from locust thoracic ganglia. J Exp Biol. 1992;170:203–233.
-
- Blagburn JM, Sosa MA, Blanco RE. Specificity of identified central synapses in the embryonic cockroach: appropriate connections form before the onset of spontaneous afferent activity. J Comp Neurol. 1996;373:511–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
