Increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by circulating polymorphonuclear neutrophils and regulation by interleukin 10 during intestinal inflammation
- PMID: 9616306
- PMCID: PMC1727082
- DOI: 10.1136/gut.42.4.470
Increased secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by circulating polymorphonuclear neutrophils and regulation by interleukin 10 during intestinal inflammation
Abstract
Background: Concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines are increased in the intestinal mucosa of patients with active inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Polymorphonuclear neutrophil granulocytes (PMN) are the most abundant cell type in intestinal lesions in IBD. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) is an important contra-inflammatory cytokine which induces downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Aims: To investigate whether PMN from patients with IBD or infectious colitis, respectively, secrete increased amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines and can be regulated by IL-10.
Methods: Secretion (ELISA) as well as corresponding mRNA levels (semiquantitative RT-PCR) of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1 beta, TNF-alpha) and of IL-1 receptor antagonist were assessed in peripheral PMN.
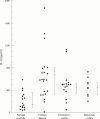
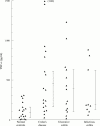
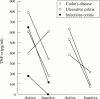
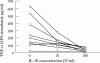
Results: PMN from patients with IBD are primed to secrete enhanced amounts of pro-inflammatory cytokines accompanied by detection of corresponding mRNAs in comparison with normal controls. This finding is not specific for IBD but rather reflects intestinal inflammation in general. IL-10 markedly inhibited proinflammatory cytokine secretion as well as corresponding mRNA concentrations.
Conclusions: PMN are an important source of pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients with intestinal inflammation and can be downregulated by IL-10.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
