Nocturnal desaturation in patients with stable heart failure
- PMID: 9616350
- PMCID: PMC1728650
- DOI: 10.1136/hrt.79.4.394
Nocturnal desaturation in patients with stable heart failure
Abstract
Objective: To determine the prevalence of sleep disordered breathing within a United Kingdom heart failure population.
Subjects: 104 patients and 21 matched normal volunteers.
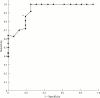
Methods: Overnight home pulse oximetry with simultaneous ECG recording in the patient group; daytime sleepiness was assessed using the Epworth sleepiness scale (ESS); 41 patients underwent polysomnography to assess the validity of oximetry as a screening test for Cheyne-Stokes respiration.
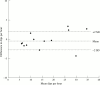
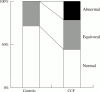
Results: Home oximetry was a good screening test for Cheyne-Stokes respiration (specificity 81%, sensitivity 87%). Patients with poorer New York Heart Association (NYHA) classes had higher sleepiness scores (p < 0.005). Twenty three patients had "abnormal" patterns of nocturnal desaturation suggestive of Cheyne-Stokes respiration. The mean (SEM) frequency of dips in Sao2 exceeding 4% was 10.3 (0.9) per hour in the patients and 4.8 (0.6) in normal controls (p < 0.005). Ejection fraction correlated negatively with dip frequency (r = -0.5, p < 0.005). The patient subgroup with > or = 15 dips/hour had a higher mean (SEM) NYHA class (3.0 (0.2) v 2.3 (0.1), p < 0.05), and experienced more ventricular ectopy (220 (76) v 78 (21) beats/hour, p < 0.05). There was no excess of serious arrhythmia.
Conclusions: Nocturnal desaturation is common in patients with treated heart failure. Low ejection fraction was related to dip frequency. Lack of correlation between dips and ESS suggests that arousal from sleep is more important than hypoxia in the aetiology of daytime sleepiness in heart failure. Overnight oximetry is a useful screening test for Cheyne-Stokes respiration in patients with known heart failure.
Figures


Comment in
-
Nocturnal desaturation in patients with stable heart failure.Heart. 1998 Dec;80(6):633-4. doi: 10.1136/hrt.80.6.633b. Heart. 1998. PMID: 10065042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Nocturnal dyspnea and atrial fibrillation predict Cheyne-Stokes respirations in patients with congestive heart failure.Arch Intern Med. 1995 Jun 26;155(12):1297-302. Arch Intern Med. 1995. PMID: 7778961
-
[Remission of nocturnal pathological respiratory patterns after orthotopic heart transplantation. A case report and overview of current status of therapy].Med Klin (Munich). 2000 Dec 15;95(12):706-11. doi: 10.1007/pl00002090. Med Klin (Munich). 2000. PMID: 11198560 Review. German.
-
Improvement of exercise capacity with treatment of Cheyne-Stokes respiration in patients with congestive heart failure.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 May;27(6):1486-90. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(96)00024-1. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8626963 Clinical Trial.
-
A randomized controlled trial of adaptive ventilation for Cheyne-Stokes breathing in heart failure.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003 Nov 1;168(9):1109-14. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200212-1476OC. Epub 2003 Aug 19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003. PMID: 12928310 Clinical Trial.
-
[Central sleep apnea syndrome and Cheyne-Stokes respiration].Ther Umsch. 2000 Jul;57(7):458-62. doi: 10.1024/0040-5930.57.7.458. Ther Umsch. 2000. PMID: 10953654 Review. German.
Cited by
-
The Long-Term Effect of Medically Enhancing Melanin Intrinsic Bioenergetics Capacity in Prematurity.Curr Genomics. 2020 Nov;21(7):525-530. doi: 10.2174/1389202921999200417172817. Curr Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33214768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cognitive impairment in heart failure with Cheyne-Stokes respiration.Heart. 2001 Jan;85(1):18-22. doi: 10.1136/heart.85.1.18. Heart. 2001. PMID: 11119454 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of nocturnal oxygen therapy in patients with chronic heart failure and central sleep apnea: CHF-HOT study.Heart Vessels. 2016 Feb;31(2):165-72. doi: 10.1007/s00380-014-0592-6. Epub 2014 Oct 28. Heart Vessels. 2016. PMID: 25348726
-
Low night-to-night variability of sleep disordered breathing in patients with stable congestive heart failure.Clin Res Cardiol. 2008 Nov;97(11):836-42. doi: 10.1007/s00392-008-0695-0. Epub 2008 Jul 21. Clin Res Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18648724
-
Determinants of excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue in adults with heart failure.Clin Nurs Res. 2012 Aug;21(3):271-93. doi: 10.1177/1054773811419842. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Clin Nurs Res. 2012. PMID: 21878581 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
