Molecular genetics of the RNA polymerase II general transcriptional machinery
- PMID: 9618449
- PMCID: PMC98922
- DOI: 10.1128/MMBR.62.2.465-503.1998
Molecular genetics of the RNA polymerase II general transcriptional machinery
Abstract
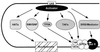
Transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) requires interaction between cis-acting promoter elements and trans-acting factors. The eukaryotic promoter consists of core elements, which include the TATA box and other DNA sequences that define transcription start sites, and regulatory elements, which either enhance or repress transcription in a gene-specific manner. The core promoter is the site for assembly of the transcription preinitiation complex, which includes RNA pol II and the general transcription fctors TBP, TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, and TFIIH. Regulatory elements bind gene-specific factors, which affect the rate of transcription by interacting, either directly or indirectly, with components of the general transcriptional machinery. A third class of transcription factors, termed coactivators, is not required for basal transcription in vitro but often mediates activation by a broad spectrum of activators. Accordingly, coactivators are neither gene-specific nor general transcription factors, although gene-specific coactivators have been described in metazoan systems. Transcriptional repressors include both gene-specific and general factors. Similar to coactivators, general transcriptional repressors affect the expression of a broad spectrum of genes yet do not repress all genes. General repressors either act through the core transcriptional machinery or are histone related and presumably affect chromatin function. This review focuses on the global effectors of RNA polymerase II transcription in yeast, including the general transcription factors, the coactivators, and the general repressors. Emphasis is placed on the role that yeast genetics has played in identifying these factors and their associated functions.
Figures
References
-
- Akoulitchev S, Makela T P, Weinberg R A, Reinberg D. Requirement for TFIIH kinase activity in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1995;377:557–560. - PubMed
-
- Alland L, Muhle R, Hou H, Jr, Potes J, Chin L, Schreiber-Agus N, DePinho R A. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 1997;387:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Apone L M, Virbasius C M A, Reese J C, Green M R. Yeast TAF(II)90 is required for cell-cycle progression through G(2)/M but not for general transcription activation. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2368–2380. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

