Expressed protein ligation: a general method for protein engineering
- PMID: 9618476
- PMCID: PMC22605
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6705
Expressed protein ligation: a general method for protein engineering
Abstract
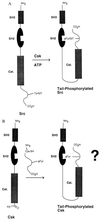
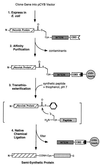
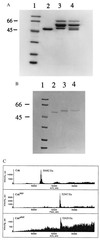
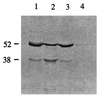
A protein semisynthesis method-expressed protein ligation-is described that involves the chemoselective addition of a peptide to a recombinant protein. This method was used to ligate a phosphotyrosine peptide to the C terminus of the protein tyrosine kinase C-terminal Src kinase (Csk). By intercepting a thioester generated in the recombinant protein with an N-terminal cysteine containing synthetic peptide, near quantitative chemical ligation of the peptide to the protein was achieved. The semisynthetic tail-phosphorylated Csk showed evidence of an intramolecular phosphotyrosine-Src homology 2 interaction and an unexpected increase in catalytic phosphoryl transfer efficiency toward a physiologically relevant substrate compared with the non-tail-phosphorylated control. This work illustrates that expressed protein ligation is a simple and powerful new method in protein engineering to introduce sequences of unnatural amino acids, posttranslational modifications, and biophysical probes into proteins of any size.
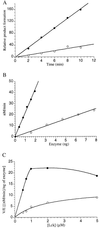
Figures
References
-
- Noren C J, Anthony-Cahill S J, Griffith M C, Schultz P G. Science. 1989;244:182–188. - PubMed
-
- Wallace C J A. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1995;6:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Witte K, Sears P, Martin R, Wong C-H. J Am Chem Soc. 1997;119:2114–2118.
-
- Jackson D Y, Burnier J, Quan C, Stanley M, Tom J, Wells J A. Science. 1994;266:243–247. - PubMed
-
- Dawson P E, Muir T W, Clark-Lewis I, Kent S B H. Science. 1994;266:776–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

