Amyrel, a paralogous gene of the amylase gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and the Sophophora subgenus
- PMID: 9618501
- PMCID: PMC22658
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6848
Amyrel, a paralogous gene of the amylase gene family in Drosophila melanogaster and the Sophophora subgenus
Abstract
We describe a gene from Drosophila melanogaster related to the alpha-amylase gene Amy. This gene, which exists as a single copy, was named Amyrel. It is strikingly divergent from Amy because the amino acid divergence is 40%. The coding sequence is interrupted by a short intron at position 655, which is unusual in amylase genes. Amyrel has also been cloned in Drosophila ananassae, Drosophila pseudoobscura, and Drosophila subobscura and is likely to be present throughout the Sophophora subgenus, but, to our knowledge, it has not been detected outside. Unexpectedly, there is a strong conservation of 5' and 3' flanking regions between Amyrel genes from different species, which is not the case for Amy and which suggests that selection acts on these regions. In contrast to the Amy genes, Amyrel is transcribed in larvae of D. melanogaster but not in adults. However, the protein has not been detected yet. Amyrel evolves about twice as fast as Amy in the several species studied. We suggest that this gene could result from a duplication of Amy followed by accelerated and selected divergence toward a new adaptation.
Figures
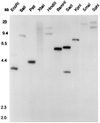





References
-
- Ohno S, Wolf U, Atkin N B. Hereditas. 1967;59:169–187. - PubMed
-
- Ohno S. Evolution by Gene Duplication. New York: Springer; 1970.
-
- Li W H, Graur D. Fundamentals of Molecular Evolution. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer; 1991.
-
- Doane W W. J Exp Zool. 1967;164:363–378. - PubMed
-
- Nakajima R, Imanaka T, Aiba S. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1986;23:355–360.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

