T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells, independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10, and important for Th2 effector function
- PMID: 9618516
- PMCID: PMC22690
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.6930
T1/ST2 is preferentially expressed on murine Th2 cells, independent of interleukin 4, interleukin 5, and interleukin 10, and important for Th2 effector function
Abstract
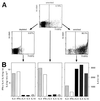
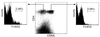
T helper (Th) cells can be categorized according to their cytokine expression. The differential induction of Th cells expressing Th1 and/or Th2 cytokines is key to the regulation of both protective and pathological immune responses. Cytokines are expressed transiently and there is a lack of stably expressed surface molecules, significant for functionally different types of Th cells. Such molecules are of utmost importance for the analysis and selective functional modulation of Th subsets and will provide new therapeutic strategies for the treatment of allergic or autoimmune diseases. To this end, we have identified potential target genes preferentially expressed in Th2 cells, expressing interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, and/or IL-10, but not interferon-gamma. One such gene, T1/ST2, is expressed stably on both Th2 clones and Th2-polarized cells activated in vivo or in vitro. T1/ST2 expression is independent of induction by IL-4, IL-5, or IL-10. T1/ST2 plays a critical role in Th2 effector function. Administration of either a mAb against T1/ST2 or recombinant T1/ST2 fusion protein attenuates eosinophilic inflammation of the airways and suppresses IL-4 and IL-5 production in vivo following adoptive transfer of Th2 cells.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

