The drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein, additionally protects drug-resistant tumor cells from multiple forms of caspase-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 9618532
- PMCID: PMC22726
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.7024
The drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein, additionally protects drug-resistant tumor cells from multiple forms of caspase-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
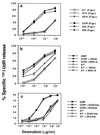
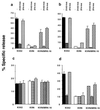
Multidrug resistance mediated by the drug efflux protein, P-glycoprotein (P-gp), is one mechanism that tumor cells use to escape death induced by chemotherapeutic agents. However, the mechanism by which P-gp confers resistance to a large variety of structurally diverse molecules has remained elusive. In this study, classical multidrug resistant human CEM and K562 tumor cell lines expressing high levels of P-gp were less sensitive to multiple forms of caspase-dependent cell death, including that mediated by cytotoxic drugs and ligation of Fas. The DNA fragmentation and membrane damage inflicted by these stimuli were defined as caspase dependent by various soluble peptide fluoromethylketone caspase inhibitors. Inhibition of P-gp function by the anti-P-gp mAb MRK-16 or verapamil could reverse resistance to these forms of cell death. Inhibition of P-gp function also enhanced drug or Fas-mediated activation of caspase-3 in drug-resistant CEM cells. By contrast, caspase-independent cell death events in the same cells, including those mediated by pore-forming proteins or intact NK cells, were not affected by P-gp expression. These observations suggest that, in addition to effluxing drugs, P-gp may play a specific role in regulating some caspase-dependent apoptotic pathways.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) overcomes multidrug resistance and induces cell death in P-glycoprotein-expressing cells.Int J Cancer. 2002 May 10;99(2):292-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10327. Int J Cancer. 2002. PMID: 11979447
-
The drug resistance proteins, multidrug resistance-associated protein and P-glycoprotein, do not confer resistance to Fas-induced cell death.Cytometry. 2001 Mar 1;43(3):189-94. doi: 10.1002/1097-0320(20010301)43:3<189::aid-cyto1048>3.0.co;2-w. Cytometry. 2001. PMID: 11170105
-
P-glycoprotein protects leukemia cells against caspase-dependent, but not caspase-independent, cell death.Blood. 1999 Feb 1;93(3):1075-85. Blood. 1999. PMID: 9920858
-
Multiple physiological functions for multidrug transporter P-glycoprotein?Trends Biochem Sci. 2000 Jan;25(1):1-6. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(99)01493-0. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000. PMID: 10637601 Review.
-
Inhibitors of p-glycoprotein--lead identification and optimisation.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005 Feb;5(2):153-63. doi: 10.2174/1389557053402729. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15720285 Review.
Cited by
-
Polydopamine-coated gold nanostar for combined antitumor and antiangiogenic therapy in multidrug-resistant breast cancer.Nanotheranostics. 2019 Jun 6;3(3):266-283. doi: 10.7150/ntno.36842. eCollection 2019. Nanotheranostics. 2019. PMID: 31263658 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin and Gastric Cancer: a Review on Mechanisms of Action.J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019 Jun;50(2):185-192. doi: 10.1007/s12029-018-00186-6. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30725357 Review.
-
Targeting Glucose Metabolism in Cancer Cells as an Approach to Overcoming Drug Resistance.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 10;15(11):2610. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112610. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application Value of Antimicrobial Peptides in Gastrointestinal Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 24;24(23):16718. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316718. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GCS overexpression is associated with multidrug resistance of human HCT-8 colon cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 16;31(1):23. doi: 10.1186/1756-9966-31-23. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 22424291 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gottesman M M, Pastan I. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. - PubMed
-
- Juliano R L, Ling V. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976;455:152–162. - PubMed
-
- Gerlach J H, Endicott J A, Juranka P F, Henderson G, Sarangi F, Deuchars K L, Ling V. Nature (London) 1986;324:485–489. - PubMed
-
- Borst P, Schinkel A H. Trends Genet. 1997;13:217–222. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

