Additional evidence for an eight-transmembrane-domain topology for Caenorhabditis elegans and human presenilins
- PMID: 9618547
- PMCID: PMC22757
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.12.7109
Additional evidence for an eight-transmembrane-domain topology for Caenorhabditis elegans and human presenilins
Abstract
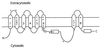
Presenilins have been implicated in the genesis of Alzheimer's disease and in facilitating LIN-12/Notch activity during development. All presenilins have multiple hydrophobic regions that could theoretically span a membrane, and a description of the membrane topology is a crucial step toward deducing the mechanism of presenilin function. Previously, we proposed an eight-transmembrane-domain model for presenilin, based on studies of the Caenorhabditis elegans SEL-12 presenilin. Here, we describe experiments that support the view that two of the hydrophobic regions of SEL-12 function as the seventh and eighth transmembrane domains. Furthermore, we have shown that human presenilin 1 behaves like SEL-12 presenilin when analyzed by our methods. Our results provide additional experimental support for the eight-transmembrane-domain model of presenilin topology.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Membrane topology of the C. elegans SEL-12 presenilin.Neuron. 1996 Nov;17(5):1015-21. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80231-7. Neuron. 1996. PMID: 8938132
-
HOP-1, a Caenorhabditis elegans presenilin, appears to be functionally redundant with SEL-12 presenilin and to facilitate LIN-12 and GLP-1 signaling.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Oct 28;94(22):12204-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.22.12204. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997. PMID: 9342387 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of SEL-12 presenilin on LIN-12 localization and function in Caenorhabditis elegans.Development. 1998 Sep;125(18):3599-606. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.18.3599. Development. 1998. PMID: 9716525
-
Function and dysfunction of the presenilins.Am J Hum Genet. 1999 Jul;65(1):7-12. doi: 10.1086/302475. Am J Hum Genet. 1999. PMID: 10364510 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
[The presenilin mystery. The research winner-by-a knockout?].C R Acad Sci III. 1999 Dec;322(12):1033-8. doi: 10.1016/s0764-4469(99)00102-x. C R Acad Sci III. 1999. PMID: 10656144 Review. French. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Advances in the cellular and molecular biology of the beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease.Neuromolecular Med. 2002;1(1):1-31. doi: 10.1385/NMM:1:1:1. Neuromolecular Med. 2002. PMID: 12025813 Review.
-
Deciphering the genesis and fate of amyloid beta-protein yields novel therapies for Alzheimer disease.J Clin Invest. 2002 Nov;110(10):1375-81. doi: 10.1172/JCI16783. J Clin Invest. 2002. PMID: 12438432 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Non-Catalytic Roles of Presenilin Throughout Evolution.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Apr 12;52(4):1177-87. doi: 10.3233/JAD-150940. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27079701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reorientation of aquaporin-1 topology during maturation in the endoplasmic reticulum.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Sep;11(9):2973-85. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.9.2973. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 10982394 Free PMC article.
-
Mice lacking both presenilin genes exhibit early embryonic patterning defects.Genes Dev. 1999 Nov 1;13(21):2801-10. doi: 10.1101/gad.13.21.2801. Genes Dev. 1999. PMID: 10557208 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

