Rapid identification of Candida albicans and other human pathogenic yeasts by using short oligonucleotides in a PCR
- PMID: 9620392
- PMCID: PMC104892
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.6.1634-1641.1998
Rapid identification of Candida albicans and other human pathogenic yeasts by using short oligonucleotides in a PCR
Abstract
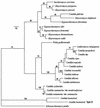
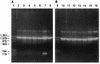
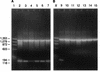
A PCR system that can quickly and accurately identify 14 species of human pathogenic yeasts was developed. The procedure distinguished between nine species of a closely related clade, Lodderomyces elongisporus, Candida parapsilosis, a new Candida sp., C. sojae, C. tropicalis, C. maltosa, C. viswanathii, C. albicans, and C. dubliniensis and between another five more divergent species, Pichia guilliermondii, C. glabrata, C. zeylanoides, C. haemulonii, and C. haemulonii type II. A rapid DNA extraction procedure that yields purified DNA in about 1 h is also described. The system uses uniform conditions with four primers for each reaction, two 40- to 50-mer universal primers that serve as a positive control and two 23- to 30-mer species-specific primers. Species-specific primers were derived from a 600-nucleotide variable region (D1/D2) at the 5' end of the large-subunit (26S) ribosomal DNA gene and were generally designed to use mismatches at the 3' end. Universal primers were developed from conserved nucleotide sequences in the small-subunit (18S) rRNA gene. In this system, a control 1,200- to 1,300-base DNA fragment was produced in all reactions and a smaller 114- to 336-base DNA fragment was produced if the chromosomal DNA from the target species was present. The PCR procedure is rapid and easy to interpret and may be used with mixed cultures.
Figures
References
-
- Ahearn D G. Yeasts pathogenic for humans. In: Kurtzman C P, Fell J W, editors. The yeasts, a taxonomic study. 4th ed. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier Science B. V.; 1998. pp. 9–14.
-
- Bodey G P. Azole antifungal agents. Clin Infect Dis. 1992;14:5161–5169. - PubMed
-
- Candian U, Hofelein C, Luthy J. Polymerase chain reaction with additional primers allows identification of amplified DNA and recognition of specific alleles. Mol Cell Probes. 1992;6:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Crampin A C, Matthews R C. Application of the polymerase chain reaction to the diagnosis of candidosis by amplification of an HSP-90 gene fragment. J Med Microbiol. 1993;39:233–238. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

