Proliferative enterocolitis associated with dual infection with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Lawsonia intracellularis in rabbits
- PMID: 9620403
- PMCID: PMC104903
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.36.6.1700-1703.1998
Proliferative enterocolitis associated with dual infection with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Lawsonia intracellularis in rabbits
Abstract
Both enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and an obligate intracellular bacterium, previously referred to as an intracellular Campylobacter-like organism and now designated Lawsonia intracellularis, have been reported as causes of enterocolitis in rabbits. An outbreak of enterocolitis in a group of rabbits, characterized by an unusually high rate of mortality, was found to be associated with dual infection with EPEC and L. intracellularis. The EPEC strain was found to have eaeA gene homology but was negative for afrA homology. The absence of the afrA gene, which encodes the structural subunit for the AF/R1 pilus, indicates that this rabbit EPEC strain is distinct from the prototypic RDEC-1 strain. This finding suggests that rabbit EPEC strains widely reported in Western Europe, which lack AF/R1 pili, are also present in rabbits in the United States. Dual infection with these two pathogens in rabbits has not been previously reported and may have contributed to the unusually high mortality observed in this outbreak.
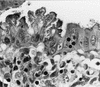
Figures



Similar articles
-
Characterization of the eaeA gene from rabbit enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strain RDEC-1 and comparison to other eaeA genes from bacteria that cause attaching-effacing lesions.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996 Nov 1;144(2-3):249-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1996.tb08538.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1996. PMID: 8900070
-
Characterization of the plasmid from Escherichia coli RDEC-1 that mediates expression of adhesin AF/R1 and evidence that AF/R1 pili promote but are not essential for enteropathogenic disease.Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1846-57. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1846-1857.1988. Infect Immun. 1988. PMID: 2899552 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Escherichia coli AF/R1 pilus operon: novel genes necessary for transcriptional regulation and for pilus-mediated adherence.Infect Immun. 1999 May;67(5):2292-8. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.5.2292-2298.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10225886 Free PMC article.
-
Presence of eaeA sequences in pathogenic and nonpathogenic Escherichia coli strains isolated from weaned rabbits.J Med Microbiol. 1994 Feb;40(2):90-4. doi: 10.1099/00222615-40-2-90. J Med Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8107067
-
Peyer's patch adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli strains in rabbits.Infect Immun. 1997 Sep;65(9):3788-93. doi: 10.1128/iai.65.9.3788-3793.1997. Infect Immun. 1997. PMID: 9284153 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Rabbit gastroenterology.Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2005 May;8(2):351-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cvex.2005.01.007. Vet Clin North Am Exot Anim Pract. 2005. PMID: 15817258 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Mutual enhancement of virulence by enterotoxigenic and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2006 Mar;74(3):1505-15. doi: 10.1128/IAI.74.3.1505-1515.2006. Infect Immun. 2006. PMID: 16495521 Free PMC article.
-
A One Health Perspective for Defining and Deciphering Escherichia coli Pathogenic Potential in Multiple Hosts.Comp Med. 2021 Feb 1;71(1):3-45. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-20-000054. Epub 2021 Jan 8. Comp Med. 2021. PMID: 33419487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coinfection with Borrelia burgdorferi and the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis alters murine immune responses, pathogen burden, and severity of Lyme arthritis.Infect Immun. 2001 May;69(5):3359-71. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.3359-3371.2001. Infect Immun. 2001. PMID: 11292759 Free PMC article.
-
Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli prevalence in laboratory rabbits.Vet Microbiol. 2013 May 3;163(3-4):395-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.01.006. Epub 2013 Jan 23. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23391439 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albert M J, Faruque S M, Ansaruzzaman M, Islam M M, Haider K, Alam K, Kabir I, Robins-Browne R. Sharing of virulence-associated properties at the phenotypic and genetic levels between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Hafnia alvei. J Med Microbiol. 1992;27:310–314. - PubMed
-
- Cantey J R, Blake R K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977;135:454–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

