Targeted disruption of SHIP leads to hemopoietic perturbations, lung pathology, and a shortened life span
- PMID: 9620849
- PMCID: PMC316868
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.11.1610
Targeted disruption of SHIP leads to hemopoietic perturbations, lung pathology, and a shortened life span
Abstract
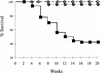
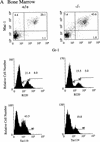
SHIP is a 145-kD SH2-containing inositol-5-phosphatase widely expressed in hemopoietic cells. It was first identified as a tyrosine phosphoprotein associated with Shc in response to numerous cytokines. SHIP has been implicated in FcgammaRIIB receptor-mediated negative signaling in B cells and mast cells and is postulated to down-regulate cytokine signal transduction in myeloid cells. To define further its role in the proliferation and differentiation of hemopoietic progenitors, as well as its function in mature cells, we have generated embryonic stem cells and mice bearing a targeted disruption of both SHIP alleles. Here we show that although SHIP null mice are viable and fertile, they fail to thrive and survival is only 40% by 14 weeks of age. Mortality is associated with extensive consolidation of the lungs resulting from infiltration by myeloid cells. Increased numbers of granulocyte-macrophage progenitors are observed in both the bone marrow and spleen of SHIP-/- mice, perhaps as a consequence of hyper-responsiveness to stimulation by macrophage-colony stimulating factor, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, interleukin-3, or Steel factor as observed in vitro. In contrast, numbers of bone marrow lymphoid and late erythroid progenitors (CFU-E) are reduced. Thus, homozygous disruption of SHIP establishes the crucial role of this molecule in modulating cytokine signaling within the hemopoietic system and provides a powerful model for further delineating its function.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Perturbed myelo/erythropoiesis in Lyn-deficient mice is similar to that in mice lacking the inhibitory phosphatases SHP-1 and SHIP-1.Blood. 2004 Dec 15;104(13):3901-10. doi: 10.1182/blood-2003-12-4396. Epub 2004 Aug 31. Blood. 2004. PMID: 15339845
-
Role of Src homology 2-containing-inositol 5'-phosphatase (SHIP) in mast cells and macrophages.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Feb;31(Pt 1):286-91. doi: 10.1042/bst0310286. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12546703 Review.
-
Positive regulation of interleukin-4-mediated proliferation by the SH2-containing inositol-5'-phosphatase.J Biol Chem. 2000 Sep 22;275(38):29275-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M002853200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10875931
-
Homeostasis and regeneration of the hematopoietic stem cell pool are altered in SHIP-deficient mice.Blood. 2003 Nov 15;102(10):3541-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-12-3939. Epub 2003 Jul 10. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12855581
-
The role of SHIP in growth factor induced signalling.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999;71(3-4):423-34. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6107(98)00049-2. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10354708 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective deletion of SHIP-1 in hematopoietic cells in mice leads to severe lung inflammation involving ILC2 cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 28;11(1):9220. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-88677-8. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33911168 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP deficiency enhances HSC proliferation and survival but compromises homing and repopulation.Blood. 2006 Jun 1;107(11):4338-45. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-12-5021. Epub 2006 Feb 7. Blood. 2006. PMID: 16467196 Free PMC article.
-
SHIP-deficient mice develop spontaneous intestinal inflammation and arginase-dependent fibrosis.Am J Pathol. 2011 Jul;179(1):180-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.03.018. Epub 2011 May 7. Am J Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21640975 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of monocytes and macrophages and their role in health and disease.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009 Jan 1;14(11):4079-102. doi: 10.2741/3514. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2009. PMID: 19273336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-4- and interleukin-13-mediated alternatively activated macrophages: roles in homeostasis and disease.Annu Rev Immunol. 2013;31:317-43. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-032712-095906. Epub 2013 Jan 3. Annu Rev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23298208 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cutler RL, Liu L, Damen JE, Krystal G. Multiple cytokines induce the tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc and its association with Grb2 in hemopoietic cells. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:21463–21465. - PubMed
-
- Damen JE, Liu L, Cutler RL, Krystal G. Erythropoietin stimulates the tyrosine phosphorylation of Shc and its association with Grb2 and a 145-Kd tyrosine phosphorylated protein. Blood. 1993;82:2296–2303. - PubMed
-
- Helgason CD, Sauvageau G, Lawrence HJ, Largman C, Humphries RK. Overexpression of HOXB4 enhances the hematopoietic potential of embryonic stem cells differentiated in vitro. Blood. 1996;87:2740–2749. - PubMed
-
- Jiao H, Yang W, Berrada K, Tabrizi M, Shultz L, Yi T. Macrophages from motheaten and viable motheaten mutant mice show increased proliferative responses to GM-CSF: Detection of potential HCP substrates in GM-CSF signal transduction. Exp Hematol. 1997;25:592–600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
