The histone acetylase PCAF is a nuclear receptor coactivator
- PMID: 9620851
- PMCID: PMC316869
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.11.1638
The histone acetylase PCAF is a nuclear receptor coactivator
Abstract
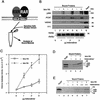
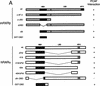
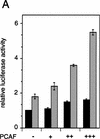
Whereas the histone acetylase PCAF has been suggested to be part of a coactivator complex mediating transcriptional activation by the nuclear hormone receptors, the physical and functional interactions between nuclear receptors and PCAF have remained unclear. Our efforts to clarify these relationships have revealed two novel properties of nuclear receptors. First, we demonstrate that the RXR/RAR heterodimer directly recruits PCAF from mammalian cell extracts in a ligand-dependent manner and that increased expression of PCAF leads to enhanced retinoid-responsive transcription. Second, we demonstrate that, in vitro, PCAF directly associates with the DNA-binding domain of nuclear receptors, independently of p300/CBP binding, therefore defining a novel cofactor interaction surface. Furthermore, our results show that dissociation of corepressors enables ligand-dependent PCAF binding to the receptors. This observation illuminates how a ligand-dependent receptor function can be propagated to regions outside the ligand-binding domain itself. On the basis of these observations, we suggest that PCAF may play a more central role in nuclear receptor function than previously anticipated.
Figures




















References
-
- Alland L, Muhle R, Hou Jr H, Potes J, Chin L, Schreiber-Agus N, DePinho RA. Role for N-CoR and histone deacetylase in Sin3-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature. 1997;387:49–55. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. The CBP coactivator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature. 1996;384:641–643. - PubMed
-
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989;56:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL, Pina B, Silverman N, Marcus GA, Agapite J, Regier JL, Triezenberg SJ, Guarente L. Genetic isolation of ADA2: A potential transcriptional adaptor required for function of certain acidic activation domains. Cell. 1992;70:251–265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
