Acyl coenzyme A synthetase from Pseudomonas fragi catalyzes the synthesis of adenosine 5'-polyphosphates and dinucleoside polyphosphates
- PMID: 9620965
- PMCID: PMC107816
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3152-3158.1998
Acyl coenzyme A synthetase from Pseudomonas fragi catalyzes the synthesis of adenosine 5'-polyphosphates and dinucleoside polyphosphates
Abstract
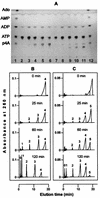
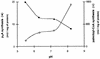
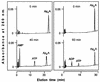
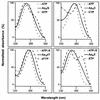
Acyl coenzyme A (CoA) synthetase (EC 6.2.1.8) from Pseudomonas fragi catalyzes the synthesis of adenosine 5'-tetraphosphate (p4A) and adenosine 5'-pentaphosphate (p5A) from ATP and tri- or tetrapolyphosphate, respectively. dATP, adenosine-5'-O-[gamma-thiotriphosphate] (ATP gamma S), adenosine(5')tetraphospho(5')adenosine (Ap4A), and adenosine(5')pentaphospho(5')adenosine (Ap5A) are also substrates of the reaction yielding p4(d)A in the presence of tripolyphosphate (P3). UTP, CTP, and AMP are not substrates of the reaction. The K(m) values for ATP and P3 are 0.015 and 1.3 mM, respectively. Maximum velocity was obtained in the presence of MgCl2 or CoCl2 equimolecular with the sum of ATP and P3. The relative rates of synthesis of p4A with divalent cations were Mg = Co > Mn = Zn >> Ca. In the pH range used, maximum and minimum activities were measured at pH values of 5.5 and 8.2, respectively; the opposite was observed for the synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA, with maximum activity in the alkaline range. The relative rates of synthesis of palmitoyl-CoA and p4A are around 10 (at pH 5.5) and around 200 (at pH 8.2). The synthesis of p4A is inhibited by CoA, and the inhibitory effect of CoA can be counteracted by fatty acids. To a lesser extent, the enzyme catalyzes the synthesis also of Ap4A (from ATP), Ap5A (from p4A), and adenosine(5')tetraphospho(5')nucleoside (Ap4N) from adequate adenylyl donors (ATP, ATP gamma S, or octanoyl-AMP) and adequate adenylyl acceptors (nucleoside triphosphates).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adenosine 5'-tetraphosphate and adenosine 5'-pentaphosphate are synthesized by yeast acetyl coenzyme A synthetase.J Bacteriol. 1994 May;176(10):2986-90. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.10.2986-2990.1994. J Bacteriol. 1994. PMID: 7910605 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of dinucleoside polyphosphates catalyzed by firefly luciferase.Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):507-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16402.x. Eur J Biochem. 1991. PMID: 1761051
-
Acyl-CoA synthetase catalyzes the synthesis of diadenosine hexaphosphate (Ap6A).Biochimie. 1999 Mar;81(3):229-33. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(99)80056-x. Biochimie. 1999. PMID: 10385004
-
Synthesis of dinucleoside polyphosphates catalyzed by firefly luciferase and several ligases.Pharmacol Ther. 2000 Aug-Sep;87(2-3):91-102. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(00)00047-4. Pharmacol Ther. 2000. PMID: 11007993 Review.
-
Metabolism of diadenosine tetraphosphate (Ap4A) and related nucleotides in plants; review with historical and general perspective.Front Biosci. 2004 May 1;9:1398-411. doi: 10.2741/1338. Front Biosci. 2004. PMID: 14977555 Review.
Cited by
-
Re-evaluation of Diadenosine Tetraphosphate (Ap4A) From a Stress Metabolite to Bona Fide Secondary Messenger.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 17;7:606807. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.606807. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33282915 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-Coumarate:coenzyme A ligase has the catalytic capacity to synthesize and reuse various (di)adenosine polyphosphates.Plant Physiol. 2003 Mar;131(3):1401-10. doi: 10.1104/pp.011684. Plant Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12644689 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Major Enzymes Involved in the Synthesis of Diadenosine Tetraphosphate and/or Adenosine Tetraphosphate in Myxococcus xanthus.Curr Microbiol. 2018 Jul;75(7):811-817. doi: 10.1007/s00284-018-1452-x. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Curr Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29468302
-
The mysterious diadenosine tetraphosphate (AP4A).Microlife. 2023 Apr 24;4:uqad016. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqad016. eCollection 2023. Microlife. 2023. PMID: 37223742 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diadenosine polyphosphates (Ap3A and Ap4A) behave as alarmones triggering the synthesis of enzymes of the phenylpropanoid pathway in Arabidopsis thaliana.FEBS Open Bio. 2011 Oct 19;1:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.fob.2011.10.002. Print 2011 Dec. FEBS Open Bio. 2011. PMID: 23650569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Fujino T, Fukuyama R, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Toh H, Suzuki H, Yamamoto T. Human long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase: structure and chromosomal location. J Biochem. 1992;111:123–128. - PubMed
-
- Airth R L, Rhodes W C, McElroy W D. The function of coenzyme A in luminescence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1958;27:519–532. - PubMed
-
- Barnes L D, Garrison P N, Siprashvili Z, Guranowski A, Robinson A K, Ingram S W, Croce C M, Ohta M, Huebner K. Fhit, a putative tumor suppressor in humans, is a dinucleoside 5′, 5′′′-P1,P3-triphosphate hydrolase. Biochemistry. 1996;35:11529–11535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

