Multiple transcriptional control of the Lactococcus lactis trp operon
- PMID: 9620968
- PMCID: PMC107819
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3174-3180.1998
Multiple transcriptional control of the Lactococcus lactis trp operon
Abstract
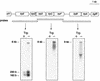
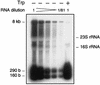
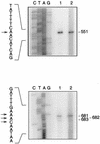
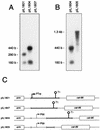
The Lactococcus lactis trpEGDCFBA operon is preceded by a noncoding leader region. Transcriptional studies of the trp operon revealed three transcripts with respective sizes of 8 kb (encompassing the entire operon), 290 bases, and 160 bases (corresponding to parts of the leader region). These transcripts most likely result from initiation at the unique Ptrp promoter, transcription termination at either T1 (upstream of the trp operon) or T2 (downstream of the trp operon), and/or processing. Three parameters were shown to differentially affect the amount of these transcripts: (i) following tryptophan depletion, the amount of the 8-kb transcript increases 300- to 500-fold; (ii) depletion in any amino acid increased transcription initiation about fourfold; and (iii) upon entry into stationary phase the amount of the 8-kb transcript decreases abruptly. The tryptophan-dependent transcription control is exerted through transcription antitermination.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcription of the trp operon in Lactococcus lactis is controlled by antitermination in the leader region.Microbiology (Reading). 1998 Aug;144 ( Pt 8):2103-2111. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-8-2103. Microbiology (Reading). 1998. PMID: 9720031
-
Tryptophan biosynthesis genes in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis.J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6563-70. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6563-6570.1992. J Bacteriol. 1992. PMID: 1400208 Free PMC article.
-
tRNATrp as a key element of antitermination in the Lactococcus lactis trp operon.Mol Microbiol. 1998 Jul;29(1):61-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00903.x. Mol Microbiol. 1998. PMID: 9701803
-
Regulation of the Bacillus subtilis trp operon by an RNA-binding protein.Mol Microbiol. 1994 Mar;11(6):991-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00377.x. Mol Microbiol. 1994. PMID: 8022289 Review.
-
Physical and genetic maps of the chromosome of the Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis strain IL1403 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris strain MG1363.Dev Biol Stand. 1995;85:597-603. Dev Biol Stand. 1995. PMID: 8586238 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Differential expression of proteins and genes in the lag phase of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis grown in synthetic medium and reconstituted skim milk.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 Feb;72(2):1173-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1173-1179.2006. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16461664 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional control of the low-temperature-inducible des gene, encoding the delta5 desaturase of Bacillus subtilis.J Bacteriol. 1999 Nov;181(22):7028-33. doi: 10.1128/JB.181.22.7028-7033.1999. J Bacteriol. 1999. PMID: 10559169 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient origin of the tryptophan operon and the dynamics of evolutionary change.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003 Sep;67(3):303-42, table of contents. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.3.303-342.2003. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003. PMID: 12966138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alternative lactose catabolic pathway in Lactococcus lactis IL1403.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005 Oct;71(10):6060-9. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.10.6060-6069.2005. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16204522 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of three bile-associated loci, bsh, pva, and btlB, to gastrointestinal persistence and bile tolerance of Listeria monocytogenes.Infect Immun. 2005 Feb;73(2):894-904. doi: 10.1128/IAI.73.2.894-904.2005. Infect Immun. 2005. PMID: 15664931 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardowski J, Ehrlich S D, Chopin A. A protein, belonging to a family of RNA-binding transcriptional anti-terminators, controls β-glucoside assimilation in Lactococcus lactis. Dev Biol Stand. 1995;85:555–559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

