Appropriate expression of filamentous phage f1 DNA replication genes II and X requires RNase E-dependent processing and separate mRNAs
- PMID: 9620980
- PMCID: PMC107831
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3245-3249.1998
Appropriate expression of filamentous phage f1 DNA replication genes II and X requires RNase E-dependent processing and separate mRNAs
Abstract
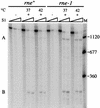
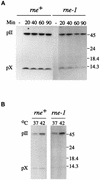
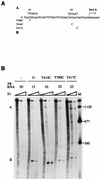
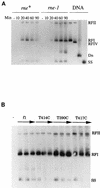
The products of in-frame overlapping genes II and X carried by the filamentous phage f1 genome are proteins with required but opposing functions in phage DNA replication. Their normal relative levels are important for continuous production of phage DNA without killing infected Escherichia coli hosts. Here we identify several factors responsible for determining the relative levels of pII and pX and that, if perturbed, alter the normal distribution of the phage DNA species in infected hosts. Translation of the two proteins is essentially relegated to separate mRNAs. The mRNAs encoding genes II and X are also differentially sensitive to cleavage dependent on rne, the gene encoding the only E. coli endo-RNase known to have a global role in mRNA stability. Whereas pII levels are limited at the level of mRNA stability, normal pX levels require transcription in sufficient amounts from the promoter for the smaller mRNA encoding only pX.
Figures


References
-
- Cashman J S, Webster R E, Steege D A. Transcription of bacteriophage f1: the major in vivo RNAs. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:2554–2562. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S N, McDowall K J. RNase E: still a wonderfully mysterious enzyme. Mol Microbiol. 1997;23:1099–1106. - PubMed
-
- Fulford W, Model P. Specificity of translational regulation by two DNA binding proteins. J Mol Biol. 1984;173:211–226. - PubMed
-
- Fulford W, Model P. Regulation of bacteriophage f1 DNA replication. I. New functions for genes II and X. J Mol Biol. 1988;203:49–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

