Characterization of the glnK-amtB operon of Azotobacter vinelandii
- PMID: 9620984
- PMCID: PMC107835
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.180.12.3260-3264.1998
Characterization of the glnK-amtB operon of Azotobacter vinelandii
Abstract
To determine whether in Azotobacter vinelandii the PII protein influences the regulation of nif gene expression in response to fluxes in the ammonium supply, the gene encoding PII was isolated and characterized. Its deduced translation product was highly similar to PII proteins from other organisms, with the greatest degree of relatedness being exhibited to the Escherichia coli glnK gene product. A gene designated amtB was found downstream of and was contranscribed with glnK as in E. coli. The AmtB protein is similar to functionally characterized ammonium transport proteins from a few other eukaryotes and one other prokaryote. glnK and amtB comprise an operon. Attempts to isolate a stable glnK mutant strain were unsuccessful, suggesting that glnK, like glnA, is an essential gene in A. vinelandii. amtB mutants were isolated, and although growth on limiting amounts of ammonium was similar in the mutant and wild-type strains, the mutants were unable to transport [14C]methylammonium.
Figures

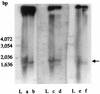
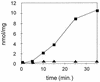
References
-
- Atkinson M R, Kamberov E S, Weiss R, Ninfa A J. Reversible uridylylation of the Escherichia coli PII signal transduction protein regulates its ability to stimulate the dephosphorylation of the transcription factor nitrogen regulator I (NRI or NtrC) J Biol Chem. 1994;269:28288–28293. - PubMed
-
- Blanco G, Drummond M, Kennedy C, Woodley P. Sequence and molecular analysis of the nifL gene of Azotobacter vinelandii. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:869–879. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

