Genetically divergent strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 use multiple coreceptors for viral entry
- PMID: 9620997
- PMCID: PMC110175
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5425-5432.1998
Genetically divergent strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 2 use multiple coreceptors for viral entry
Abstract
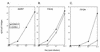
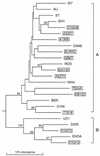
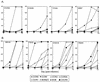
Several members of the seven-transmembrane chemokine receptor family have been shown to serve, with CD4, as coreceptors for entry by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). While coreceptor usage by HIV-1 primary isolates has been studied by several groups, there is only limited information available concerning coreceptor usage by primary HIV-2 isolates. In this study, we have analyzed coreceptor usage of 15 primary HIV-2 isolates, using lymphocytes from a donor with nonfunctional CCR5 (CCR5 -/-; homozygous 32-bp deletion). Based on the infections of PBMCs, seven of these primary isolates had an absolute requirement for CCR5 expression, whereas the remaining eight exhibited a broader coreceptor usage. All CCR5-requiring isolates were non-syncytium inducing, whereas isolates utilizing multiple coreceptors were syncytium inducing. Blocking experiments using known ligands for chemokine receptors provided indirect evidence for additional coreceptor utilization by primary HIV-2 isolates. Analysis of GHOST4 cell lines expressing various chemokine receptors (CCR1, CCR2b, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5, CXCR4, BONZO, and BOB) further defined specific coreceptor usage of primary HIV-2 isolates. The receptors used included CXCR4, CCR1-5, and the recently described receptors BONZO and BOB. However, the efficiency at which the coreceptors were utilized varied greatly among the various isolates. Analysis of V3 envelope sequences revealed no specific motif that correlated with coreceptor usage. Our data demonstrate that primary HIV-2 isolates are capable of using a broad range of coreceptors for productive infection in vitro. Additionally, our data suggest that expanded coreceptor usage by HIV-2 may correlate with disease progression.
Figures
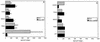
References
-
- Albert J, Stalhandske P, Marquina S, Karis J, Fouchier R A, Norby E, Chiodi F. Biological phenotype of HIV type 2 isolates correlates with V3 genotype. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1996;12:821–828. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder C C, Feng Y, Kennedy P E, Murphy P M, Berger E A. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, and MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272:1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Alkhatib G, Liao F, Berger E A, Farber J M, Pedan K W C. A new SIV co-receptor, STRL33. Nature. 1997;388:238. - PubMed
-
- Andreasson P A, Dias F, Naucler A, Andersson S, Biberfeld G. A prospective study of vertical transmission of HIV-2 in Bissau, Guinea-Bissau. AIDS. 1993;7:989–993. - PubMed
-
- Berger, E. A. 1997. HIV entry and tropism: the chemokine receptor connection. AIDS 11(Suppl. A): S3–S16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

