The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gN homolog BLRF1 encodes a 15-kilodalton glycoprotein that cannot be authentically processed unless it is coexpressed with the EBV gM homolog BBRF3
- PMID: 9621013
- PMCID: PMC110206
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5559-5564.1998
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gN homolog BLRF1 encodes a 15-kilodalton glycoprotein that cannot be authentically processed unless it is coexpressed with the EBV gM homolog BBRF3
Abstract
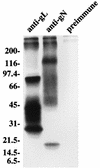
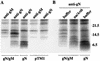
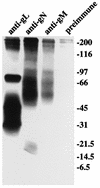
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) homolog of the conserved herpesvirus glycoprotein gN is predicted to be encoded by the BLRF1 open reading frame (ORF). Antipeptide antibody to a sequence corresponding to residues in the predicted BLRF1 ORF immunoprecipitated a doublet of approximately 8 kDa from cells expressing the BLRF1 ORF as a recombinant protein. In addition, four glycosylated proteins of 113, 84, 48, and 15 kDa could be immunoprecipitated from virus-producing cells by the same antibody. The 15-kDa species was the mature form of gN, which carried alpha2,6-sialic acid residues. The remaining glycoproteins which associated with gN were products of the BBRF3 ORF of EBV, which encodes the EBV gM homolog. The 8-kDa doublet seen in cells expressing recombinant gN comprised precursors of the mature 15-kDa gN. Coexpression of EBV gM with EBV gN was required for authentic processing of the 8-kDa forms to the 15-kDa form.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus that lacks glycoprotein gN is impaired in assembly and infection.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(23):11162-72. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.23.11162-11172.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11070013 Free PMC article.
-
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) BZLF2 gene product associates with the gH and gL homologs of EBV and carries an epitope critical to infection of B cells but not of epithelial cells.J Virol. 1995 Jul;69(7):3987-94. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.7.3987-3994.1995. J Virol. 1995. PMID: 7539502 Free PMC article.
-
Human herpesvirus-8 glycoprotein B interacts with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) glycoprotein 110 but fails to complement the infectivity of EBV mutants.Virology. 1998 Nov 25;251(2):402-13. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9412. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9837804
-
Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp85 associates with the BKRF2 gene product and is incompletely processed as a recombinant protein.Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):387-96. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1388. Virology. 1993. PMID: 8393232
-
Bovine herpesvirus 4: genomic organization and relationship with two other gammaherpesviruses, Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus saimiri.Vet Microbiol. 1996 Nov;53(1-2):79-89. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(96)01236-9. Vet Microbiol. 1996. PMID: 9011000 Review.
Cited by
-
Fusion of Epstein-Barr virus with epithelial cells can be triggered by αvβ5 in addition to αvβ6 and αvβ8, and integrin binding triggers a conformational change in glycoproteins gHgL.J Virol. 2011 Dec;85(24):13214-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05580-11. Epub 2011 Sep 28. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21957301 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular biology of pseudorabies virus: impact on neurovirology and veterinary medicine.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005 Sep;69(3):462-500. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.69.3.462-500.2005. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16148307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycoprotein M of herpes simplex virus 1 is incorporated into virions during budding at the inner nuclear membrane.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(2):800-12. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01756-06. Epub 2006 Nov 1. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17079321 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxy-terminal domain of glycoprotein N of human cytomegalovirus is required for virion morphogenesis.J Virol. 2007 May;81(10):5212-24. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01463-06. Epub 2007 Jan 17. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17229708 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes simplex virus 1 gN partners with gM to modulate the viral fusion machinery.J Virol. 2015 Feb;89(4):2313-23. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03041-14. Epub 2014 Dec 10. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25505065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baer R, Bankier A T, Biggin M D, Deininger P L, Farrell P J, Gibson T J, Hatfull G, Hudson G S, Satchwell S C, Seguin C, Tuffnell P S, Barrell B G. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984;310:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

