The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gN homolog BLRF1 encodes a 15-kilodalton glycoprotein that cannot be authentically processed unless it is coexpressed with the EBV gM homolog BBRF3
- PMID: 9621013
- PMCID: PMC110206
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5559-5564.1998
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) gN homolog BLRF1 encodes a 15-kilodalton glycoprotein that cannot be authentically processed unless it is coexpressed with the EBV gM homolog BBRF3
Abstract
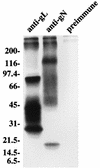
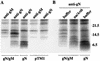
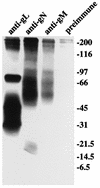
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) homolog of the conserved herpesvirus glycoprotein gN is predicted to be encoded by the BLRF1 open reading frame (ORF). Antipeptide antibody to a sequence corresponding to residues in the predicted BLRF1 ORF immunoprecipitated a doublet of approximately 8 kDa from cells expressing the BLRF1 ORF as a recombinant protein. In addition, four glycosylated proteins of 113, 84, 48, and 15 kDa could be immunoprecipitated from virus-producing cells by the same antibody. The 15-kDa species was the mature form of gN, which carried alpha2,6-sialic acid residues. The remaining glycoproteins which associated with gN were products of the BBRF3 ORF of EBV, which encodes the EBV gM homolog. The 8-kDa doublet seen in cells expressing recombinant gN comprised precursors of the mature 15-kDa gN. Coexpression of EBV gM with EBV gN was required for authentic processing of the 8-kDa forms to the 15-kDa form.
Figures





References
-
- Baer R, Bankier A T, Biggin M D, Deininger P L, Farrell P J, Gibson T J, Hatfull G, Hudson G S, Satchwell S C, Seguin C, Tuffnell P S, Barrell B G. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984;310:207–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

