Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated transgene integration into neurons and other nondividing cell targets
- PMID: 9621054
- PMCID: PMC110396
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.5919-5926.1998
Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated transgene integration into neurons and other nondividing cell targets
Abstract
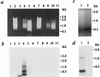
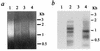
The site-specific integration of wild-type adeno-associated virus (wtAAV) into the human genome is a very attractive feature for the development of AAV-based gene therapy vectors. However, knowledge about integration of wtAAV, as well as currently configured recombinant AAV (rAAV) vectors, is limited. By using a modified Alu-PCR technique to amplify and sequence the vector-cellular junctions, we provide the first direct evidence both in vitro and in vivo of rAAV-mediated transgene integration in several types of nondividing cells, including neurons. This novel technique will be highly useful for further delineating the mechanisms underlying AAV-mediated integration, including issues of frequency, site preference, and DNA rearrangement in human as well as animal cells. Results from these studies should be beneficial for the development of the next generation of gene delivery vectors.
Figures


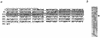
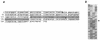
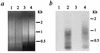
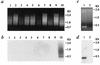
References
-
- Berns K I, Linden R M. The cryptic life style of adeno-associated virus. Bioessays. 1995;17:237–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

