The native form and maturation process of hepatitis C virus core protein
- PMID: 9621068
- PMCID: PMC110410
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.6048-6055.1998
The native form and maturation process of hepatitis C virus core protein
Abstract
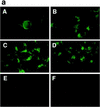
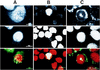
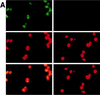
The maturation and subcellular localization of hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein were investigated with both a vaccinia virus expression system and CHO cell lines stably transformed with HCV cDNA. Two HCV core proteins, with molecular sizes of 21 kDa (p21) and 23 kDa (p23), were identified. The C-terminal end of p23 is amino acid 191 of the HCV polyprotein, and p21 is produced as a result of processing between amino acids 174 and 191. The subcellular localization of the HCV core protein was examined by confocal laser scanning microscopy. Although HCV core protein resided predominantly in the cytoplasm, it was also found in the nucleus and had the same molecular size as p21 in both locations, as determined by subcellular fractionation. The HCV core proteins had different immunoreactivities to a panel of monoclonal antibodies. Antibody 5E3 stained core protein in both the cytoplasm and the nucleus, C7-50 stained core protein only in the cytoplasm, and 499S stained core protein only in the nucleus. These results clearly indicate that the p23 form of HCV core protein is processed to p21 in the cytoplasm and that the core protein in the nucleus has a higher-order structure different from that of p21 in the cytoplasm. HCV core protein in sera of patients with HCV infection was analyzed in order to determine the molecular size of genuinely processed HCV core protein. HCV core protein in sera was found to have exactly the same molecular weight as the p21 protein. These results suggest that p21 core protein is a component of native viral particles.
Figures



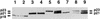


References
-
- Choo Q-L, Kuo G, Weiner A J, Overby L R, Bradley D W, Houghton M. Isolation of cDNA derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244:359–362. - PubMed
-
- Esteban J I, Esteban R, Viladomiu L, Lopez-Talavera J C, Gonzalez A, Hernandez J M, Roget M, Vargas V, Genesca J, Buti M, Guardia J. Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain. Lancet. 1989;ii:294–296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

