Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virion entry by dominant-negative Hck
- PMID: 9621101
- PMCID: PMC110455
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.72.7.6257-6259.1998
Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virion entry by dominant-negative Hck
Abstract
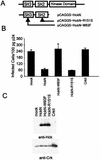
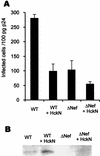
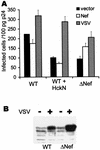
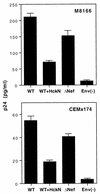
To study the role of Src family tyrosine kinases in infection with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1), we constructed an Hck mutant, HckN, that hinders signaling from wild-type Hck. HIV-1 produced in HckN-expressing cells was significantly less infectious to HeLa-CD4-LTR-beta-gal (MAGI) cells than HIV-1 produced in mock-transfected cells. The inhibitory effect of HckN was compensated for by the expression of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. Finally, we found that the HIV-1 produced in the HckN-expressing cells entered into the cells less efficiently than did the control HIV-1. These results suggest that the Src family tyrosine kinases regulate entry of HIV-1 into target cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hck SH3 domain-dependent abrogation of Nef-induced class 1 MHC down-regulation.Eur J Immunol. 2001 Aug;31(8):2382-7. doi: 10.1002/1521-4141(200108)31:8<2382::aid-immu2382>3.0.co;2-k. Eur J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11500821
-
Induction of activator protein 1 (AP-1) in macrophages by human immunodeficiency virus type-1 NEF is a cell-type-specific response that requires both hck and MAPK signaling events.J Mol Biol. 1999 Jul 2;290(1):21-35. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1999.2849. J Mol Biol. 1999. PMID: 10388555
-
Oligomerization is required for HIV-1 Nef-induced activation of the Src family protein-tyrosine kinase, Hck.Biochemistry. 2004 Dec 21;43(50):15775-84. doi: 10.1021/bi048712f. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 15595833
-
Use of the two-hybrid system to identify cellular partners of the HIV1 Nef protein.Res Virol. 1997 Jan-Feb;148(1):71-3. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2516(97)81918-8. Res Virol. 1997. PMID: 9017839 Review. No abstract available.
-
Cell-dependent functional roles of HIV-1 Nef for virus replication (review).Int J Mol Med. 1999 Apr;3(4):427-30. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.3.4.427. Int J Mol Med. 1999. PMID: 10085418 Review.
Cited by
-
Src kinase mediates productive endocytic sorting of reovirus during cell entry.J Virol. 2011 Apr;85(7):3203-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02056-10. Epub 2011 Jan 19. J Virol. 2011. PMID: 21248042 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 infection of T cells and macrophages are differentially modulated by virion-associated Hck: a Nef-dependent phenomenon.Viruses. 2013 Sep 18;5(9):2235-52. doi: 10.3390/v5092235. Viruses. 2013. PMID: 24051604 Free PMC article.
-
A Truncated Nef Peptide from SIVcpz Inhibits the Production of HIV-1 Infectious Progeny.Viruses. 2016 Jul 7;8(7):189. doi: 10.3390/v8070189. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27399760 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Nef down-regulates the hemochromatosis protein HFE, manipulating cellular iron homeostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Aug 2;102(31):11017-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504823102. Epub 2005 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16043695 Free PMC article.
-
Secreted phospholipases A(2), a new class of HIV inhibitors that block virus entry into host cells.J Clin Invest. 1999 Sep;104(5):611-8. doi: 10.1172/JCI6915. J Clin Invest. 1999. PMID: 10487775 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barone M V, Courtneidge S. myc but not fos rescue of PDGF signalling block caused by kinase-inactive src. Nature (London) 1995;378:509–512. - PubMed
-
- Briand G, Barbeau B, Corbeil J, Tremblay M. Enhancement of HIV-1-induced syncytium formation in T cells by the tyrosyl kinase p56lck. Virology. 1997;231:10–19. - PubMed
-
- Cohen D I, Tani Y, Tian H, Boone E, Samelson L E, Lane H C. Participation of tyrosine phosphorylation in the cytopathic effect of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Science. 1992;256:542–545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

