Mode of action of sulfanilyl fluoroquinolones
- PMID: 9624501
- PMCID: PMC105629
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.42.6.1495
Mode of action of sulfanilyl fluoroquinolones
Abstract
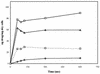
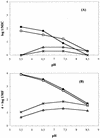
The mode of action of sulfanilyl fluoroquinolones (NSFQs) was investigated with NSFQ-104, NSFQ-105, and some structurally related compounds. Evidence arising from interactions with p-aminobenzoic acid and trimethoprim suggested that a sulfonamidelike mechanism of action makes little or no contribution to the in vitro activity of NSFQs. NSFQ-105 showed an activity that inhibits gyrase-catalyzed DNA supercoiling that is similar to the activity of other fluoroquinolones. Also, NSFQ-105 uptake was decreased by the presence of Mg2+ and increased by a lower pH. These results indicate that NSFQs having only one ionizable group could exhibit more favorable kinetics of access to the bacterial cell than zwitterionic fluoroquinolones.
Figures
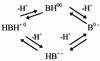
References
-
- Allemandi D A, Alovero F L, Manzo R H. In vitro activity of new sulphanilyl fluoroquinolones against Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1994;34:261–264. - PubMed
-
- Alovero F L, Allemandi D A, Nieto M J, Mazzieri M R, Manzo R H. Program and abstracts of the II Congreso Federación Farmacéutica Sudamericana. Santiago, Chile. 1995. Efecto del Mg2+ sobre la actividad de NSFQ-104 y NSFQ-105 a distintos pHs, abstr. 95.
-
- Dámaso D, editor. Antibacterianos. Madrid, Spain: Marketing Pharm, S.A.; 1990.
-
- De Benedetti P G. Molecular modeling and quantitative structure-activity analysis of antibacterial sulfanilamides and sulfones. Prog Drug Res. 1991;36:361–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

