Interleukin (IL)-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) requirement for optimal induction of multiple IL-1 signaling pathways and IL-6 production
- PMID: 9625767
- PMCID: PMC2212370
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2073
Interleukin (IL)-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) requirement for optimal induction of multiple IL-1 signaling pathways and IL-6 production
Abstract
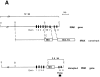
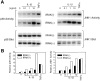
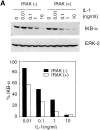
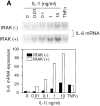
Interleukin (IL)-1 is a proinflammatory cytokine with pleiotropic effects in inflammation. IL-1 binding to its receptor triggers a cascade of signaling events, including activation of the stress-activated mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinases, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 MAP kinase, as well as transcription factor nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB). IL-1 signaling results in cellular responses through induction of inflammatory gene products such as IL-6. One of the earliest events in IL-1 signaling is the rapid interaction of IL-1 receptor-associated kinases, IRAK and IRAK-2, with the receptor complex. The relative roles of IRAK and IRAK-2 in IL-1 signaling pathways and subsequent cellular responses have not been previously determined. To evaluate the importance of IRAK in IL-1 signaling, IRAK-deficient mouse fibroblast cells were prepared and studied. Here we report that IL-1-mediated activation of JNK, p38, and NF-kappaB were all reduced in embryonic fibroblasts deficient in IRAK expression. In addition, IL-6 production in response to IL-1 was also dramatically reduced in IRAK-deficient embryonic fibroblasts and in skin fibroblasts prepared from IRAK-deficient mice. Our results demonstrate that IRAK plays an essential proximal role in coordinating multiple IL-1 signaling pathways for optimal induction of cellular responses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Effects of IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) expression on IL-1 signaling are independent of its kinase activity.FEBS Lett. 1999 Apr 1;448(1):81-5. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00322-1. FEBS Lett. 1999. PMID: 10217414
-
Defective interleukin (IL)-18-mediated natural killer and T helper cell type 1 responses in IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK)-deficient mice.J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 5;189(7):1129-38. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1129. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10190904 Free PMC article.
-
Severe impairment of interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signalling in mice lacking IRAK-4.Nature. 2002 Apr 18;416(6882):750-6. doi: 10.1038/nature736. Epub 2002 Mar 31. Nature. 2002. PMID: 11923871
-
Functional diversity and regulation of different interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) family members.Mol Cell. 2003 Feb;11(2):293-302. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00053-4. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12620219 Review.
-
[In vitro and in vivo study of regulation mechanisms of type I interleukin-1 receptor].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2001 Jan;121(1):9-21. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.121.9. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2001. PMID: 11201166 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The TNF family member 4-1BBL sustains inflammation by interacting with TLR signaling components during late-phase activation.Sci Signal. 2013 Oct 1;6(295):ra87. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2004431. Sci Signal. 2013. PMID: 24084649 Free PMC article.
-
The IRAK-catalysed activation of the E3 ligase function of Pellino isoforms induces the Lys63-linked polyubiquitination of IRAK1.Biochem J. 2008 Jan 1;409(1):43-52. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071365. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 17997719 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the genetics of systemic lupus erythematosus.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010 May;6(3):461-79. doi: 10.1586/eci.10.8. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20441431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 plays an essential role for Toll-like receptor (TLR)7- and TLR9-mediated interferon-{alpha} induction.J Exp Med. 2005 Mar 21;201(6):915-23. doi: 10.1084/jem.20042372. Epub 2005 Mar 14. J Exp Med. 2005. PMID: 15767370 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoic acid selectively activates the ERK2 but not JNK/SAPK or p38 MAP kinases when inducing myeloid differentiation.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1999 Oct;35(9):527-32. doi: 10.1007/s11626-999-0063-z. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 1999. PMID: 10548434
References
-
- Dinarello CA. Biologic basis for interleukin–1 in disease. Blood. 1996;87:2095–2147. - PubMed
-
- Glaccum MB, Stocking KL, Charrier K, Smith JL, Willis CR, Maliszewski C, Livingston DJ, Peschon JJ, Morrissey PJ. Phenotypic and functional characterization of mice that lack the type I receptor for IL-1. J Immunol. 1997;159:3364–3371. - PubMed
-
- Labow M, Shuster D, Zetterstrom M, Nunes P, Terry R, Cullinan EB, Bartfai T, Solorzano C, Moldawer LL, Chizzonite R, Mclntyre KW. Absence of IL-1 signaling and reduced inflammatory response in IL-1 type I receptor–deficient mice. J Immunol. 1997;159:2452–2461. - PubMed
-
- Leon LR, Conn CA, Glaccum M, Kluger MJ. IL-1 type I receptor mediates acute phase response to turpentine, but not lipopolysaccharide, in mice. Am J Physiol. 1996;271:R1668–R1675. - PubMed
-
- Zheng H, Fletcher D, Kozak W, Jiang M, Hofmann KJ, Conn CA, Soszynski D, Grabiec C, Trumbauer ME, Shaw A, et al. Resistance to fever induction and impaired acute phase response in interleukin-1β–deficient mice. Immunity. 1995;3:9–19. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

