The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)
- PMID: 9625770
- PMCID: PMC2212359
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.187.12.2097
The human toll signaling pathway: divergence of nuclear factor kappaB and JNK/SAPK activation upstream of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6)
Abstract
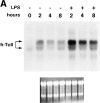
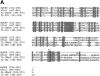
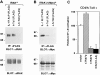
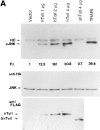
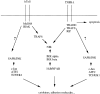
The human homologue of Drosophila Toll (hToll) is a recently cloned receptor of the interleukin 1 receptor (IL-1R) superfamily, and has been implicated in the activation of adaptive immunity. Signaling by hToll is shown to occur through sequential recruitment of the adapter molecule MyD88 and the IL-1R-associated kinase. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-activated factor 6 (TRAF6) and the nuclear factor kappaB (NF-kappaB)-inducing kinase (NIK) are both involved in subsequent steps of NF-kappaB activation. Conversely, a dominant negative version of TRAF6 failed to block hToll-induced activation of stress-activated protein kinase/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases, thus suggesting an early divergence of the two pathways.
Figures




References
-
- Medzhitov R, Janeway A., Jr Innate immunity: the virtues of a nonclonal system of recognition. Cell. 1997;91:295–298. - PubMed
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA. A human homologue of the DrosophilaToll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Lemaitre B, Nicolas E, Michaut L, Reichart J-M, Hoffmann JA. The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophilaadults. Cell. 1996;86:973–983. - PubMed
-
- Greenfeder SA, Nunes P, Kwee L, Labow M, Chizzonite RA, Ju G. Molecular cloning and characterization of a second subunit of the interleukin 1 receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:13757–13765. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

