Control of pulsatile 5-HT/insulin secretion from single mouse pancreatic islets by intracellular calcium dynamics
- PMID: 9625872
- PMCID: PMC2231018
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.135bz.x
Control of pulsatile 5-HT/insulin secretion from single mouse pancreatic islets by intracellular calcium dynamics
Abstract
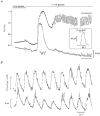
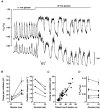
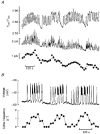
1. Glucose-induced insulin release from single islets of Langerhans is pulsatile. We have investigated the correlation between changes in cytosolic free calcium concentration ([Ca2+]i) and oscillatory insulin secretion from single mouse islets, in particular examining the basis for differences in secretory responses to intermediate and high glucose concentrations. Insulin release was monitored in real time through the amperometric detection of the surrogate insulin marker 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) via carbon fibre microelectrodes. The [Ca2+]i was simultaneously recorded by whole-islet fura-2 microfluorometry. 2. In 82 % of the experiments, exposure to 11 mM glucose evoked regular high-frequency (average, 3.4 min-1) synchronous oscillations in amperometric current and [Ca2+]i. In the remaining experiments (18 %), 11 mM glucose induced an oscillatory pattern consisting of high-frequency [Ca2+]i oscillations that were superimposed on low-frequency (average, 0.32 min-1) [Ca2+]i waves. Intermittent high-frequency [Ca2+]i oscillations gave rise to a similar pattern of pulsatile 5-HT release. 3. Raising the glucose concentration from 11 to 20 mM increased the duration of the steady-state [Ca2+]i oscillations without increasing their amplitude. In contrast, both the duration and amplitude of the associated 5-HT transients were increased by glucose stimulation. The amount of 5-HT released per secretion cycle was linearly related to the duration of the underlying [Ca2+]i oscillations in both 11 and 20 mM glucose. The slopes of the straight lines were identical, indicating that there is no significant difference between the ability of calcium oscillations to elicit 5-HT/insulin release in 11 and 20 mM glucose. 4. In situ 5-HT microamperometry has the potential to resolve the high-frequency oscillatory component of the second phase of glucose-induced insulin secretion. This component appears to reflect primarily the duration of the underlying [Ca2+]i oscillations, suggesting that glucose metabolism and/or access to glucose metabolites is not rate limiting to fast pulsatile insulin release.
Figures
References
-
- Barbosa RM, Rosário LM, Brett CMA, Oliveira-Brett AM. Electrochemical studies of zinc in zinc-insulin solution. Analyst. 1996a;121:1789–1793. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa RM, Silva AM, Tomé AR, Stamford JA, Santos RM, Rosário LM. Real time electrochemical detection of 5-HT/insulin secretion from single pancreatic islets: effect of glucose and K+ depolarization. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1996b;228:100–104. - PubMed
-
- Bergsten P. Slow and fast oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in pancreatic islets correspond to pulsatile insulin release. American Journal of Physiology. 1995;268:E282–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

