Interaction of vault particles with estrogen receptor in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell
- PMID: 9628887
- PMCID: PMC2132791
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.6.1301
Interaction of vault particles with estrogen receptor in the MCF-7 breast cancer cell
Abstract
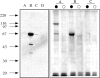
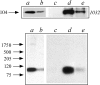
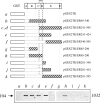
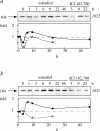
A 104-kD protein was coimmunoprecipitated with the estrogen receptor from the flowtrough of a phosphocellulose chromatography of MCF-7 cell nuclear extract. mAbs to this protein identified several cDNA clones coding for the human 104-kD major vault protein. Vaults are large ribonucleoprotein particles of unknown function present in all eukaryotic cells. They have a complex morphology, including several small molecules of RNA, but a single protein species, the major vault protein, accounts for >70% of their mass. Their shape is reminiscent of the nucleopore central plug, but no proteins of known function have been described to interact with them. Western blot analysis of vaults purified on sucrose gradient showed the presence of estrogen receptor co-migrating with the vault peak. The AER317 antibody to estrogen receptor coimmunoprecipitated the major vault protein and the vault RNA also in the 20,000 g supernatant fraction. Reconstitution experiments of estrogen receptor fragments with the major vault protein mapped the site of the interaction between amino acids 241 and 280 of human estrogen receptor, where the nuclear localization signal sequences are located. Estradiol treatment of cells increased the amount of major vault protein present in the nuclear extract and coimmunoprecipitated with estrogen receptor, whereas the anti-estrogen ICI182,780 had no effect. The hormone-dependent interaction of vaults with estrogen receptor was reproducible in vitro and was prevented by sodium molybdate. Antibodies to progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors were able to coimmunoprecipitate the major vault protein. The association of nuclear receptors with vaults could be related to their intracellular traffic.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The formation of vault-tubes: a dynamic interaction between vaults and vault PARP.J Cell Sci. 2003 Nov 1;116(Pt 21):4391-400. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00749. Epub 2003 Sep 16. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 13130096
-
Models of estrogen receptor regulation by estrogens and antiestrogens in breast cancer cell lines.Cancer Res. 1996 May 15;56(10):2321-30. Cancer Res. 1996. PMID: 8625307
-
The La RNA-binding protein interacts with the vault RNA and is a vault-associated protein.J Biol Chem. 2002 Oct 25;277(43):41282-6. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M206980200. Epub 2002 Aug 23. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12196535
-
The vault complex.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003 Sep;60(9):1828-37. doi: 10.1007/s00018-003-3030-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2003. PMID: 14523546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vaults and the major vault protein: novel roles in signal pathway regulation and immunity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Jan;66(1):43-61. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8364-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 18759128 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Major vault protein is expressed along the nucleus-neurite axis and associates with mRNAs in cortical neurons.Cereb Cortex. 2009 Jul;19(7):1666-77. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhn203. Epub 2008 Nov 21. Cereb Cortex. 2009. PMID: 19029061 Free PMC article.
-
IL-25 promotes cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells by activating NF-κB signaling pathway to increase of major vault protein.Cancer Med. 2019 Jul;8(7):3491-3501. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2213. Epub 2019 May 1. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31044552 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant major vault protein is targeted to neuritic tips of PC12 cells.J Cell Biol. 1999 Mar 22;144(6):1163-72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.144.6.1163. J Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10087261 Free PMC article.
-
Steroid-induced androgen receptor-oestradiol receptor beta-Src complex triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation.EMBO J. 2000 Oct 16;19(20):5406-17. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.20.5406. EMBO J. 2000. PMID: 11032808 Free PMC article.
-
Human Vault RNAs: Exploring Their Potential Role in Cellular Metabolism.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 6;25(7):4072. doi: 10.3390/ijms25074072. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbondanza C, De Falco A, Nigro V, Medici N, Armetta I, Molinari AM, Moncharmont B, Puca GA. Characterization and epitope mapping of a new panel of monoclonal antibodies to estradiol receptor. Steroids. 1993;58:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel, F.M., R. Breint, R.E. Kingston, D.D. Moore, J.G. Seidman, J.G. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1996. Current Protocols in Molecolar Biology. Vol. 3. Wiley & Sons Inc., New York.
-
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989;56:335–344. - PubMed
-
- Beato M, Herrlich P, Schütz G. Steroid hormone receptors: many actors in search for a plot. Cell. 1995;83:851–857. - PubMed
-
- Binart N, Chambraud B, Dumas B, Rowlands DA, Bigogne C, Levin JM, Garnier J, Baulieu EE, Catelli MG. The cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of chick heat shock protein Mr90,000 (HSP 90) reveals a “DNA like” structure: potential site of interaction with steroid receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989;159:140–147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

