GalNAc-alpha-O-benzyl inhibits NeuAcalpha2-3 glycosylation and blocks the intracellular transport of apical glycoproteins and mucus in differentiated HT-29 cells
- PMID: 9628888
- PMCID: PMC2132799
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.141.6.1311
GalNAc-alpha-O-benzyl inhibits NeuAcalpha2-3 glycosylation and blocks the intracellular transport of apical glycoproteins and mucus in differentiated HT-29 cells
Abstract
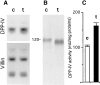
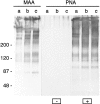
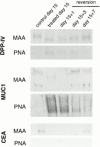
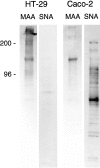
Exposure for 24 h of mucus-secreting HT-29 cells to the sugar analogue GalNAc-alpha-O-benzyl results in inhibition of Galbeta1-3GalNAc:alpha2,3-sialyltransferase, reduced mucin sialylation, and inhibition of their secretion (Huet, G., I. Kim, C. de Bolos, J.M. Loguidice, O. Moreau, B. Hémon, C. Richet, P. Delannoy, F.X. Real., and P. Degand. 1995. J. Cell Sci. 108:1275-1285). To determine the effects of prolonged inhibition of sialylation, differentiated HT-29 populations were grown under permanent exposure to GalNAc-alpha-O-benzyl. This results in not only inhibition of mucus secretion, but also in a dramatic swelling of the cells and the accumulation in intracytoplasmic vesicles of brush border-associated glycoproteins like dipeptidylpeptidase-IV, the mucin-like glycoprotein MUC1, and carcinoembryonic antigen which are no longer expressed at the apical membrane. The block occurs beyond the cis-Golgi as substantiated by endoglycosidase treatment and biosynthesis analysis. In contrast, the polarized expression of the basolateral glycoprotein GP 120 is not modified. Underlying these effects we found that (a) like in mucins, NeuAcalpha2-3Gal-R is expressed in the terminal position of the oligosaccharide species associated with the apical, but not the basolateral glycoproteins of the cells, and (b) treatment with GalNAc-alpha-O-benzyl results in an impairment of their sialylation. These effects are reversible upon removal of the drug. It is suggested that alpha2-3 sialylation is involved in apical targeting of brush border membrane glycoproteins and mucus secretion in HT-29 cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
GalNAc-alpha -O-benzyl inhibits sialylation of de Novo synthesized apical but not basolateral sialoglycoproteins and blocks lysosomal enzyme processing in a post-trans-Golgi network compartment.J Biol Chem. 2000 Jun 23;275(25):18785-93. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M000510200. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10751388
-
Permanent exposure of mucin-secreting HT-29 cells to benzyl-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminide induces abnormal O-glycosylation of mucins and inhibits constitutive and stimulated MUC5AC secretion.Biochem J. 1998 Aug 15;334 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):283-95. doi: 10.1042/bj3340283. Biochem J. 1998. PMID: 9693131 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of the glycosylation and alteration in the intracellular trafficking of mucins and other glycoproteins by GalNAcalpha-O-bn in mucosal cell lines: an effect mediated through the intracellular synthesis of complex GalNAcalpha-O-bn oligosaccharides.Front Biosci. 2001 Oct 1;6:D1235-44. doi: 10.2741/gouyer. Front Biosci. 2001. PMID: 11578961 Review.
-
Benzyl-N-acetyl-alpha-D-galactosaminide inhibits the sialylation and the secretion of mucins by a mucin secreting HT-29 cell subpopulation.Glycoconj J. 1996 Oct;13(5):717-26. doi: 10.1007/BF00702335. Glycoconj J. 1996. PMID: 8909998
-
Involvement of glycosylation in the intracellular trafficking of glycoproteins in polarized epithelial cells.Biochimie. 2003 Mar-Apr;85(3-4):323-30. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(03)00056-7. Biochimie. 2003. PMID: 12770771 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous analyses of N-linked and O-linked glycans of ovarian cancer cells using solid-phase chemoenzymatic method.Clin Proteomics. 2017 Jan 13;14:3. doi: 10.1186/s12014-017-9137-1. eCollection 2017. Clin Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28100988 Free PMC article.
-
Steric shielding of surface epitopes and impaired immune recognition induced by the ebola virus glycoprotein.PLoS Pathog. 2010 Sep 9;6(9):e1001098. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001098. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20844579 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into the biological roles of mucin-type O-glycosylation.Glycoconj J. 2009 Apr;26(3):325-34. doi: 10.1007/s10719-008-9162-4. Epub 2008 Aug 10. Glycoconj J. 2009. PMID: 18695988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Core 2 Mucin-Type O-Glycan Is Related to EPEC and EHEC O157:H7 Adherence to Human Colon Carcinoma HT-29 Epithelial Cells.Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Jul;60(7):1977-90. doi: 10.1007/s10620-015-3548-5. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Dig Dis Sci. 2015. PMID: 25701318
-
Overexpression of alpha2,3 sialyltransferase in neuroblastoma cells results in an upset in the glycosylation process.Glycoconj J. 1999 Oct;16(10):649-57. doi: 10.1023/a:1007033218309. Glycoconj J. 1999. PMID: 10972143
References
-
- Braulke T, Mach L, Hoflack B, Glossl J. Biosynthesis and endocytosis of lysosomal enzymes in human colon carcinoma SW1116 cells: impaired internalization of plasma membrane-associated cation-independent mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992;298:176–181. - PubMed
-
- Byrd, J.C., R. Dahiya, J. Huang, and Y.S. Kim. 1995. Inhibition of mucin synthesis by benzyl-α-GalNAc in KATO III gastric cancer and Caco-2 colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Cancer. 31A:1498–1505. - PubMed
-
- Capon C, Laboisse CL, Wieruszeki JM, Maoret JJ, Augeron C, Fournet B. Oligosaccharide structures of mucins secreted by the human colonic cancer cell line CL.16E. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:19248–19257. - PubMed
-
- Chang ML, Eddy RL, Shows TB, Lau JTY. Three genes that encode human β-galactosidase α-2,3-sialyltransferases. Structural analysis and chromosomal lapping studies. Glycobiology. 1995;5:319–325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

