Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector: use for transgene expression and anterograde tract tracing in the CNS
- PMID: 9630611
- PMCID: PMC4961038
- DOI: 10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00169-3
Recombinant adeno-associated virus vector: use for transgene expression and anterograde tract tracing in the CNS
Abstract
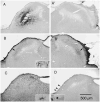
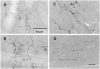
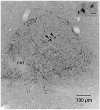
We used a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector (AAV) to deliver a foreign gene, green fluorescent protein (GFP), into mature neurons in adult rat CNS in vivo. Microinjections of AAV as small as 50 nl transduced hundreds of neurons at the injection site. There was virtually no retrograde transport as fewer than one neuron per brain was found distant from the injection site that exhibited GFP immunoreactivity. The gene product, GFP, filled the entire neuronal cytoplasmic compartment; GFP immunoreactivity was robust in cell bodies, axons, and nerve terminals. There was no tissue damage at the injection sites or pathogenicity indicated by changes in astrocytic or microglial markers. There was no inflammatory response as judged by leukocytic invasion. Gene expression in transduced cells was robust and apparently permanent: there was no evidence of phenotypic reversion up to 12 weeks following infection. AAV is an excellent vector for introducing foreign genes into mature CNS neurons. Not only might it be an ideal vehicle for gene therapy, but also the GFP-containing AAV presents a new strategy for tracing long axonal pathways in the CNS, which is difficult with current tracers (PHAL, biotinylated dextrans).
Copyright 1998 Elsevier Science B.V.
Figures

References
-
- Bernard JF, Alden M, Besson JM. The organization of the efferent projections from the pontine parabrachial area to the amygdaloid complex: a phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHA-L) study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1993;329:201–229. - PubMed
-
- Chamberlin NL, Saper CB. Differential distribution of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits in the parabrachial nucleus of the rat. Neuroscience. 1995;68:435–443. - PubMed
-
- Du B, Wu P, Boldt-Houle DM, Terwilliger EF. Efficient trans-duction of human neurons with an adeno-associated virus vector. Gene Ther. 1996;3:254–261. - PubMed
-
- Earle KL, Mitrofanis J. Identification of transient microglial cell colonies in the forebrain white matter of developing rats. J Comp Neurol. 1997;387:371–384. - PubMed
-
- Feil K, Herbert H. Topographic organization of spinal and trigemi-nal somatosensory pathways to the rat parabrachial and Kolliker– Fuse nuclei. J Comp Neurol. 1995;353:506–528. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

