Inhibition of murine splenic and mucosal lymphocyte function by enteric bacterial products
- PMID: 9632575
- PMCID: PMC108322
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.7.3120-3127.1998
Inhibition of murine splenic and mucosal lymphocyte function by enteric bacterial products
Abstract
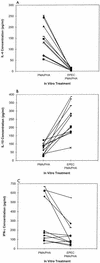
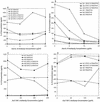
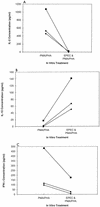
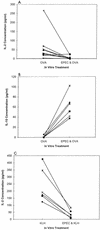
Previously we showed that lysates of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) inhibit lymphokine production by mitogen-activated human peripheral blood and lamina propria mononuclear cells. The aims of the present study were to determine whether EPEC-inhibitory factors have similar effects on murine lymphoid populations in order to further delineate the mechanisms of alteration of cytokine production. Preexposure to EPEC lysates inhibited mitogen-stimulated interleukin-2 (IL-2), IL-4, and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) production by murine spleen cells, but IL-10 production was increased. The inhibition was not due to increased apoptosis and was not blocked by neutralizating antibodies against IL-10 or transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta). EPEC lysates also inhibited mitogen-stimulated IL-2 and IFN-gamma production by CD11b-depleted spleen cells, IL-2 and IL-4 production by intraepithelial and Peyer's patch lymphocytes, IL-2 production by the human T-cell line Jurkat, and antigen-stimulated IL-2 production by murine spleen cells. Lysates obtained from Shiga-like toxin-producing E. coli, E. coli RDEC-1, Citrobacter rodentium, and an EPEC espB insertion mutant all inhibited IL-2 and IL-4 production by mitogen-stimulated lymphoid cells. In conclusion, lysates of EPEC and related bacteria directly inhibit cytokine production by lymphoid cells from multiple sites by a mechanism that does not increase apoptosis or result from secondary effects of IL-10 or TGF-beta.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Products of enteropathogenic E. coli inhibit lymphokine production by gastrointestinal lymphocytes.Am J Physiol. 1996 Nov;271(5 Pt 1):G841-8. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1996.271.5.G841. Am J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8944699
-
Role of bacterial intimin in colonic hyperplasia and inflammation.Science. 1999 Jul 23;285(5427):588-91. doi: 10.1126/science.285.5427.588. Science. 1999. PMID: 10417389
-
Intimin from enteropathogenic Escherichia coli restores murine virulence to a Citrobacter rodentium eaeA mutant: induction of an immunoglobulin A response to intimin and EspB.Infect Immun. 1996 Dec;64(12):5315-25. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.12.5315-5325.1996. Infect Immun. 1996. PMID: 8945583 Free PMC article.
-
Products of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli inhibit lymphocyte activation and lymphokine production.Infect Immun. 1995 Jun;63(6):2248-54. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.6.2248-2254.1995. Infect Immun. 1995. PMID: 7768605 Free PMC article.
-
Reciprocal IFN-gamma and TGF-beta responses regulate the occurrence of mucosal inflammation.Immunol Today. 1997 Feb;18(2):61-4. doi: 10.1016/s0167-5699(97)01000-1. Immunol Today. 1997. PMID: 9057354 Review.
Cited by
-
Mice lacking T and B lymphocytes develop transient colitis and crypt hyperplasia yet suffer impaired bacterial clearance during Citrobacter rodentium infection.Infect Immun. 2002 Apr;70(4):2070-81. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.4.2070-2081.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 11895973 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Escherichia coli Shiga Toxins in STEC Colonization of Cattle.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;12(9):607. doi: 10.3390/toxins12090607. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lack of a role of cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 toxin from Escherichia coli in bacterial pathogenicity and host cytokine response in infected germfree piglets.Infect Immun. 2000 Feb;68(2):839-47. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.2.839-847.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 10639454 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of innate cytokine responses by products of Helicobacter pylori.Infect Immun. 2000 Nov;68(11):6265-72. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.11.6265-6272.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 11035734 Free PMC article.
-
Efa1 influences colonization of the bovine intestine by shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli serotypes O5 and O111.Infect Immun. 2002 Sep;70(9):5158-66. doi: 10.1128/IAI.70.9.5158-5166.2002. Infect Immun. 2002. PMID: 12183566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arai T, Matsui K. A purified protein from Salmonella typhimurium inhibits high-affinity interleukin-2 receptor expression on CTLL-2 cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 1997;17:155–160. - PubMed
-
- Cantey J R, Blake R K. Diarrhea due to Escherichia coli in the rabbit: a novel mechanism. J Infect Dis. 1977;135:454–462. - PubMed
-
- Donnenberg M S, Kaper J B, Finlay B B. Interactions between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and host epithelial cells. Trends Microbiol. 1997;5:109–114. - PubMed
-
- Donnenberg M S, Donohue-Rolfe A, Keusch G T. Epithelial cell invasion: an overlooked property of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) associated with the EPEC adherence factor. J Infect Dis. 1989;160:452–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

