Potential role of epithelial cell-derived histone H1 proteins in innate antimicrobial defense in the human gastrointestinal tract
- PMID: 9632593
- PMCID: PMC108340
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.66.7.3255-3263.1998
Potential role of epithelial cell-derived histone H1 proteins in innate antimicrobial defense in the human gastrointestinal tract
Abstract
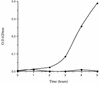
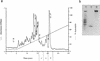
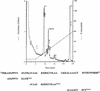
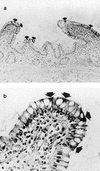
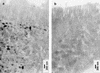
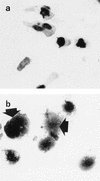
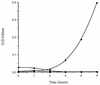
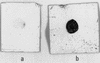
In the human gastrointestinal tract, microorganisms are present in large numbers in the colon but are sparse in the proximal small intestine. In this study, we have shown that acid extracts of fresh human terminal ileal mucosal samples mediate antimicrobial activity. Following cation-exchange chromatography, one of the eluted fractions demonstrated antibacterial activity against bacteria normally resident in the human colonic lumen. This activity was further fractionated by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography and identified as histone H1 and its fragments. We have also shown that in tissue sections, immunoreactive histone H1 is present in the cytoplasm of villus epithelial cells. In vitro culturing of detached (from the basement membrane) villus epithelial cells led to the release of antimicrobial histone H1 proteins, while the cells demonstrated ultrastructural features of programmed cell death. Our studies suggest that cytoplasmic histone H1 may provide protection against penetration by microorganisms into villus epithelial cells. Moreover, intestinal epithelial cells released into the lumen may mediate antimicrobial activity by releasing histone H1 proteins and their fragments.
Figures

References
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Edman P. Method of determination of the amino acid sequence in peptides. Acta Chem Scand. 1950;4:283–293.
-
- Erlandsen S L, Parsons J A, Taylor T D. Ultrastructural immunocytochemical localization of lysozyme in the Paneth cells of man. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974;22:401–413. - PubMed
-
- Fields P I, Groisman E A, Heffron F. A Salmonella locus that controls resistance to microbicidal proteins from phagocytic cells. Science. 1989;243:1059–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

