AP1 regulation of proliferation and initiation of apoptosis in erythropoietin-dependent erythroid cells
- PMID: 9632752
- PMCID: PMC108952
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.3699
AP1 regulation of proliferation and initiation of apoptosis in erythropoietin-dependent erythroid cells
Abstract
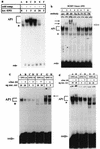
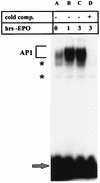
The transcription factor AP1 has been implicated in the induction of apoptosis in cells in response to stress factors and growth factor withdrawal. We report here that AP1 is necessary for the induction of apoptosis following hormone withdrawal in the erythropoietin (EPO)-dependent erythroid cell line HCD57. AP1 DNA binding activity increased upon withdrawal of HCD57 cells from EPO. A dominant negative AP1 mutant rendered these cells resistant to apoptosis induced by EPO withdrawal and blocked the downregulation of Bcl-XL. JunB is a major binding protein in the AP1 complex observed upon EPO withdrawal; JunB but not c-Jun was present in the AP1 complex 3 h after EPO withdrawal in HCD57 cells, with a concurrent increase in junB message and protein. Furthermore, analysis of AP1 DNA binding activity in an apoptosis-resistant subclone of HCD57 revealed a lack of induction in AP1 DNA binding activity and no change in junB mRNA levels upon EPO withdrawal. In addition, we determined that c-Jun and AP1 activities correlated with EPO-induced proliferation and/or protection from apoptosis. AP1 DNA binding activity increased over the first 3 h following EPO stimulation of HCD57 cells, and suppression of AP1 activity partially inhibited EPO-induced proliferation. c-Jun but not JunB was present in the AP1 complex 3 h after EPO addition. These results implicate AP1 in the regulation of proliferation and survival of erythroid cells and suggest that different AP1 factors may play distinct roles in both triggering apoptosis (JunB) and protecting erythroid cells from apoptosis (c-Jun).
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of JunB in erythroid differentiation.J Biol Chem. 2002 Feb 15;277(7):4859-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107243200. Epub 2001 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11726656
-
JNK and p38 are activated by erythropoietin (EPO) but are not induced in apoptosis following EPO withdrawal in EPO-dependent HCD57 cells.Blood. 2000 Aug 1;96(3):933-40. Blood. 2000. PMID: 10910907
-
A novel mechanism of cooperation between c-Kit and erythropoietin receptor. Stem cell factor induces the expression of Stat5 and erythropoietin receptor, resulting in efficient proliferation and survival by erythropoietin.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jan 12;276(2):1099-106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M007442200. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11042182
-
Unraveling distinct intracellular signals that promote survival and proliferation: study of erythropoietin, stem cell factor, and constitutive signaling in leukemic cells.J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2000 Feb;9(1):21-9. doi: 10.1089/152581600319586. J Hematother Stem Cell Res. 2000. PMID: 10738968 Review.
-
Role of c-Kit and erythropoietin receptor in erythropoiesis.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005 Apr;54(1):63-75. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2004.11.005. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2005. PMID: 15780908 Review.
Cited by
-
Differential Regulation of Bcl-xL Gene Expression by Corticosterone, Progesterone, and Retinoic Acid.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016 Jun;30(6):309-16. doi: 10.1002/jbt.21795. Epub 2016 Feb 25. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26915917 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of benzopyrene diol epoxide-induced apoptosis by cadmium(II) is AP-1-independent: role of extracelluler signal related kinase.Chem Biol Interact. 2008 Mar 10;172(1):72-80. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2007.11.002. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Chem Biol Interact. 2008. PMID: 18093576 Free PMC article.
-
Retinal Neuroprotective Effects of Flibanserin, an FDA-Approved Dual Serotonin Receptor Agonist-Antagonist.PLoS One. 2016 Jul 22;11(7):e0159776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0159776. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27447833 Free PMC article.
-
Low-grade neuroinflammation due to chronic sleep deprivation results in anxiety and learning and memory impairments.Mol Cell Biochem. 2018 Dec;449(1-2):63-72. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3343-7. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29549603
-
Anti-tumor activity of curcumin against androgen-independent prostate cancer cells via inhibition of NF-κB and AP-1 pathway in vitro.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011 Aug;31(4):530. doi: 10.1007/s11596-011-0485-1. Epub 2011 Aug 7. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2011. PMID: 21823017
References
-
- Adler V, Fuchs S Y, Kim J, Kraft A, King M P, Pelling J, Ronai Z. Jun-NH2-terminal kinase activation mediated by UV-induced DNA lesions in melanoma and fibroblast cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1995;6:1437–1446. - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Allegretto E A, Okino S T, Hattori K, Boyle W J, Hunter T, Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988;332:166–171. - PubMed
-
- Angel P, Imagawa M, Chiu R, Stein B, Imbra R J, Rahmsdorf H J, Jonat C, Herrlich P, Karin M. Phorbolester-inducible genes contain a common cis-element recognized by the TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987;49:729–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
