Spa2p interacts with cell polarity proteins and signaling components involved in yeast cell morphogenesis
- PMID: 9632790
- PMCID: PMC108990
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4053
Spa2p interacts with cell polarity proteins and signaling components involved in yeast cell morphogenesis
Abstract
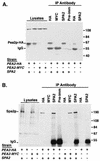
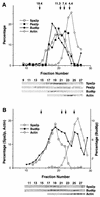
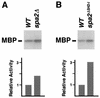
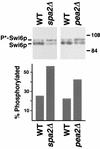
The yeast protein Spa2p localizes to growth sites and is important for polarized morphogenesis during budding, mating, and pseudohyphal growth. To better understand the role of Spa2p in polarized growth, we analyzed regions of the protein important for its function and proteins that interact with Spa2p. Spa2p interacts with Pea2p and Bud6p (Aip3p) as determined by the two-hybrid system; all of these proteins exhibit similar localization patterns, and spa2Delta, pea2Delta, and bud6Delta mutants display similar phenotypes, suggesting that these three proteins are involved in the same biological processes. Coimmunoprecipitation experiments demonstrate that Spa2p and Pea2p are tightly associated with each other in vivo. Velocity sedimentation experiments suggest that a significant portion of Spa2p, Pea2p, and Bud6p cosediment, raising the possibility that these proteins form a large, 12S multiprotein complex. Bud6p has been shown previously to interact with actin, suggesting that the 12S complex functions to regulate the actin cytoskeleton. Deletion analysis revealed that multiple regions of Spa2p are involved in its localization to growth sites. One of the regions involved in Spa2p stability and localization interacts with Pea2p; this region contains a conserved domain, SHD-II. Although a portion of Spa2p is sufficient for localization of itself and Pea2p to growth sites, only the full-length protein is capable of complementing spa2 mutant defects, suggesting that other regions are required for Spa2p function. By using the two-hybrid system, Spa2p and Bud6p were also found to interact with components of two mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways important for polarized cell growth. Spa2p interacts with Ste11p (MAPK kinase [MEK] kinase) and Ste7p (MEK) of the mating signaling pathway as well as with the MEKs Mkk1p and Mkk2p of the Slt2p (Mpk1p) MAPK pathway; for both Mkk1p and Ste7p, the Spa2p-interacting region was mapped to the N-terminal putative regulatory domain. Bud6p interacts with Ste11p. The MEK-interacting region of Spa2p corresponds to the highly conserved SHD-I domain, which is shown to be important for mating and MAPK signaling. spa2 mutants exhibit reduced levels of pheromone signaling and an elevated level of Slt2p kinase activity. We thus propose that Spa2p, Pea2p, and Bud6p function together, perhaps as a complex, to promote polarized morphogenesis through regulation of the actin cytoskeleton and signaling pathways.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The Spa2-related protein, Sph1p, is important for polarized growth in yeast.J Cell Sci. 1998 Feb;111 ( Pt 4):479-94. doi: 10.1242/jcs.111.4.479. J Cell Sci. 1998. PMID: 9443897
-
Spa2p functions as a scaffold-like protein to recruit the Mpk1p MAP kinase module to sites of polarized growth.Curr Biol. 2002 Oct 1;12(19):1698-703. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01186-7. Curr Biol. 2002. PMID: 12361575
-
Protein-protein interactions in the yeast PKC1 pathway: Pkc1p interacts with a component of the MAP kinase cascade.Mol Gen Genet. 1996 Jul 26;251(6):682-91. doi: 10.1007/BF02174117. Mol Gen Genet. 1996. PMID: 8757399
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human.Physiol Rev. 1999 Jan;79(1):143-80. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1999.79.1.143. Physiol Rev. 1999. PMID: 9922370 Review.
-
Messengers for morphogenesis: inositol polyphosphate signaling and yeast pseudohyphal growth.Curr Genet. 2019 Feb;65(1):119-125. doi: 10.1007/s00294-018-0874-0. Epub 2018 Aug 12. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30101372 Review.
Cited by
-
Coupling of PAK-interacting exchange factor PIX to GIT1 promotes focal complex disassembly.Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Sep;20(17):6354-63. doi: 10.1128/MCB.20.17.6354-6363.2000. Mol Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10938112 Free PMC article.
-
Septin ring assembly requires concerted action of polarisome components, a PAK kinase Cla4p, and the actin cytoskeleton in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2004 Dec;15(12):5329-45. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e04-03-0254. Epub 2004 Sep 15. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15371547 Free PMC article.
-
Ras1-induced hyphal development in Candida albicans requires the formin Bni1.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Oct;4(10):1712-24. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.10.1712-1724.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 16215178 Free PMC article.
-
The 'interactome' of the Knr4/Smi1, a protein implicated in coordinating cell wall synthesis with bud emergence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Genet Genomics. 2006 Mar;275(3):217-30. doi: 10.1007/s00438-005-0082-8. Epub 2005 Dec 16. Mol Genet Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16362369
-
Modular coherence of protein dynamics in yeast cell polarity system.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 May 3;108(18):7647-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1017567108. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21502521 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
