Functional conservation of the transportin nuclear import pathway in divergent organisms
- PMID: 9632798
- PMCID: PMC108998
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4141
Functional conservation of the transportin nuclear import pathway in divergent organisms
Abstract
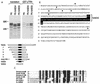
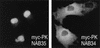
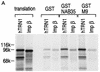
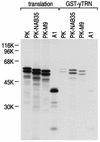
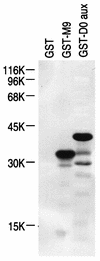
Human transportin1 (hTRN1) is the nuclear import receptor for a group of pre-mRNA/mRNA-binding proteins (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins [hnRNP]) represented by hnRNP A1, which shuttle continuously between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. hTRN1 interacts with the M9 region of hnRNP A1, a 38-amino-acid domain rich in Gly, Ser, and Asn, and mediates the nuclear import of M9-bearing proteins in vitro. Saccharomyces cerevisiae transportin (yTRN; also known as YBR017c or Kap104p) has been identified and cloned. To understanding the nuclear import mediated by yTRN, we searched with a yeast two-hybrid system for proteins that interact with it. In an exhaustive screen of the S. cerevisiae genome, the most frequently selected open reading frame was the nuclear mRNA-binding protein, Nab2p. We delineated a ca.-50-amino-acid region in Nab2p, termed NAB35, which specifically binds yTRN and is similar to the M9 motif. NAB35 also interacts with hTRN1 and functions as a nuclear localization signal in mammalian cells. Interestingly, yTRN can also mediate the import of NAB35-bearing proteins into mammalian nuclei in vitro. We also report on additional substrates for TRN as well as sequences of Drosophila melanogaster, Xenopus laevis, and Schizosaccharomyces pombe TRNs. Together, these findings demonstrate that both the M9 signal and the nuclear import machinery utilized by the transportin pathway are conserved in evolution.
Figures



References
-
- Aitchison J D, Blobel G, Rout M P. Kap104p: a karyopherin involved in the nuclear transport of messenger RNA binding proteins. Science. 1996;274:624–627. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff F R, Görlich D. RanBP1 is crucial for the release of RanGTP from importin β-related nuclear transport factors. FEBS Lett. 1997;419:249–254. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff, F. R., S. Nakielny, and G. Dreyfuss. Unpublished results.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
