The capacity of polyomavirus enhancer binding protein 2alphaB (AML1/Cbfa2) to stimulate polyomavirus DNA replication is related to its affinity for the nuclear matrix
- PMID: 9632801
- PMCID: PMC109001
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4165
The capacity of polyomavirus enhancer binding protein 2alphaB (AML1/Cbfa2) to stimulate polyomavirus DNA replication is related to its affinity for the nuclear matrix
Abstract
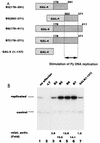
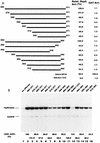
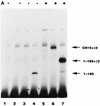
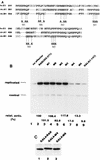
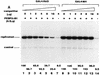
The nuclear matrix is thought to play an important role in the DNA replication of eukaryotic cells, although direct evidence for such a role is still lacking. A nuclear matrix-associated transcription factor, polyomavirus (Py) enhancer binding protein 2alphaB1 (PEBP2alphaB1) (AML1/Cbfa2), was found to stimulate Py replication through its cognate binding site. The minimal replication activation domain (RAD) was identified between amino acid (aa) 302 and aa 371 by using a fusion protein containing the GAL4 DNA binding domain (GAL4-RAD). In addition, the region showed affinity for the nuclear matrix and, on the basis of competition studies, binding activity for one or more proteins involved in the initiation of Py DNA replication. A leukemogenic chimeric protein, AML1/ETO(MTG8), which does not contain this region of PEBP2alphaB1/AML1, was also localized in the nuclear matrix fraction and competed for nuclear matrix association with PEBP2alphaB1 and GAL4-RAD. Moreover, AML1/ETO inhibited Py DNA replication stimulated by PEBP2alphaB1 and GAL4-RAD. The inhibition was specific for replication mediated by PEBP2alphaB1 and GAL4-RAD, and proportional to the degree of loss of these activators from the nuclear matrix, suggesting a requirement for nuclear matrix targeting in the stimulation of Py DNA replication by RAD. These results are the first to suggest a molecular link between the initiation of DNA replication and the nuclear matrix compartment.
Figures

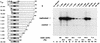













Similar articles
-
Transcription factor Runx1 recruits the polyomavirus replication origin to replication factories.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Apr 1;100(5):1313-23. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21115. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17063494
-
Intrinsic transcriptional activation-inhibition domains of the polyomavirus enhancer binding protein 2/core binding factor alpha subunit revealed in the presence of the beta subunit.Mol Cell Biol. 1998 May;18(5):2444-54. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.5.2444. Mol Cell Biol. 1998. PMID: 9566865 Free PMC article.
-
The yeast GAL4 protein transactivates the polyomavirus origin of DNA replication in mouse cells.J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3496-503. doi: 10.1128/JVI.65.7.3496-3503.1991. J Virol. 1991. PMID: 1645781 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of the t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukaemia.Semin Cancer Biol. 1993 Dec;4(6):369-75. Semin Cancer Biol. 1993. PMID: 8142622 Review.
-
The AML1 gene: a transcription factor involved in the pathogenesis of myeloid and lymphoid leukemias.Haematologica. 1997 May-Jun;82(3):364-70. Haematologica. 1997. PMID: 9234595 Review.
Cited by
-
Atrophin-1, the dentato-rubral and pallido-luysian atrophy gene product, interacts with ETO/MTG8 in the nuclear matrix and represses transcription.J Cell Biol. 2000 Sep 4;150(5):939-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.150.5.939. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10973986 Free PMC article.
-
Context-dependent modulation of replication activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae autonomously replicating sequences by transcription factors.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Nov;19(11):7428-35. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.11.7428. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10523631 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome-protein interactions in polyomavirus virions.J Virol. 2004 Jan;78(1):513-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.78.1.513-519.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 14671132 Free PMC article.
-
MLL-AFX requires the transcriptional effector domains of AFX to transform myeloid progenitors and transdominantly interfere with forkhead protein function.Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Sep;22(18):6542-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.18.6542-6552.2002. Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12192052 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TAZ as a binding partner of the polyomavirus T antigens.J Virol. 2004 Nov;78(22):12657-64. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.22.12657-12664.2004. J Virol. 2004. PMID: 15507652 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amati B B, Gasser S M. Chromosomal ARS and CEN elements bind specifically to the yeast nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1988;54:967–978. - PubMed
-
- Bae S C, Takahashi E, Zhang Y W, Ogawa E, Shigesada K, Namba Y, Sataka M, Ito Y. Cloning, mapping and expression of PEBP2αC, a third gene encoding the mammalian Runt domain. Gene. 1995;159:245–248. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
