Activated polo-like kinase Plx1 is required at multiple points during mitosis in Xenopus laevis
- PMID: 9632810
- PMCID: PMC109010
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4262
Activated polo-like kinase Plx1 is required at multiple points during mitosis in Xenopus laevis
Abstract
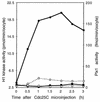
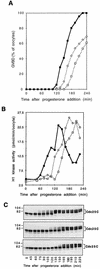
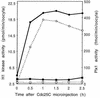
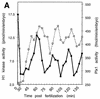
Entry into mitosis depends upon activation of the dual-specificity phosphatase Cdc25C, which dephosphorylates and activates the cyclin B-Cdc2 complex. Previous work has shown that the Xenopus polo-like kinase Plx1 can phosphorylate and activate Cdc25C in vitro. In the work presented here, we demonstrate that Plx1 is activated in vivo during oocyte maturation with the same kinetics as Cdc25C. Microinjection of wild-type Plx1 into Xenopus oocytes accelerated the rate of activation of Cdc25C and cyclin B-Cdc2. Conversely, microinjection of either an antibody against Plx1 or kinase-dead Plx1 significantly inhibited the activation of Cdc25C and cyclin B-Cdc2. This effect could be reversed by injection of active Cdc25C, indicating that Plx1 is upstream of Cdc25C. However, injection of Cdc25C, which directly activates cyclin B-Cdc2, also caused activation of Plx1, suggesting that a positive feedback loop exists in the Plx1 activation pathway. Other experiments show that injection of Plx1 antibody into early embryos, which do not require Cdc25C for the activation of cyclin B-Cdc2, resulted in an arrest of cleavage that was associated with monopolar spindles. These results demonstrate that in Xenopus laevis, Plx1 plays important roles both in the activation of Cdc25C at the initiation of mitosis and in spindle assembly at late stages of mitosis.
Figures



References
-
- Amon A, Surana U, Muroff I, Nasmyth K. Regulation of p34CDC28 tyrosine phosphorylation is not required for entry into mitosis in S. cerevisiae. Nature. 1992;355:368–371. - PubMed
-
- Dasso M, Newport J W. Completion of DNA replication is monitored by a feedback system that controls the initiation of mitosis in vitro: studies in Xenopus. Cell. 1990;61:811–823. - PubMed
-
- Dunphy W G, Kumagai A. The cdc25 protein contains an intrinsic phosphatase activity. Cell. 1991;67:189–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
