Calcium and S100B regulation of p53-dependent cell growth arrest and apoptosis
- PMID: 9632811
- PMCID: PMC109011
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4272
Calcium and S100B regulation of p53-dependent cell growth arrest and apoptosis
Abstract
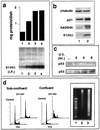
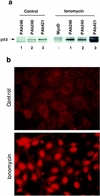
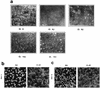
In glial C6 cells constitutively expressing wild-type p53, synthesis of the calcium-binding protein S100B is associated with cell density-dependent inhibition of growth and apoptosis in response to UV irradiation. A functional interaction between S100B and p53 was first demonstrated in p53-negative mouse embryo fibroblasts (MEF cells) by sequential transfection with the S100B and the temperature-sensitive p53Val135 genes. We show that in MEF cells expressing a low level of p53Val135, S100B cooperates with p53Val135 in triggering calcium-dependent cell growth arrest and cell death in response to UV irradiation at the nonpermissive temperature (37.5 degreesC). Calcium-dependent growth arrest of MEF cells expressing S100B correlates with specific nuclear accumulation of the wild-type p53Val135 conformational species. S100B modulation of wild-type p53Val135 nuclear translocation and functions was confirmed with the rat embryo fibroblast (REF) cell line clone 6, which is transformed by oncogenic Ha-ras and overexpression of p53Val135. Ectopic expression of S100B in clone 6 cells restores contact inhibition of growth at 37.5 degreesC, which also correlates with nuclear accumulation of the wild-type p53Val135 conformational species. Moreover, a calcium ionophore mediates a reversible G1 arrest in S100B-expressing REF (S100B-REF) cells at 37.5 degreesC that is phenotypically indistinguishable from p53-mediated G1 arrest at the permissive temperature (32 degreesC). S100B-REF cells proceeding from G1 underwent apoptosis in response to UV irradiation. Our data support a model in which calcium signaling and S100B cooperate with the p53 pathways of cell growth inhibition and apoptosis.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Concerted regulation of wild-type p53 nuclear accumulation and activation by S100B and calcium-dependent protein kinase C.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Oct;19(10):7168-80. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.10.7168. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10490652 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium-dependent interaction of S100B with the C-terminal domain of the tumor suppressor p53.J Biol Chem. 1999 Apr 9;274(15):10539-44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.15.10539. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10187847
-
The protein kinase C activator, phorbol ester, cooperates with the wild-type p53 species of Ras-transformed embryo fibroblasts growth arrest.J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29579-87. J Biol Chem. 1994. PMID: 7961944
-
A search for inhibitors of S100B, a member of the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007 Jun;7(6):609-16. doi: 10.2174/138955707780859422. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17584159 Review.
-
Design of Inhibitors for S100B.Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5(12):1093-108. doi: 10.2174/156802605774370865. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16248785 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting S100B in Cerebral Ischemia and in Alzheimer's Disease.Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2010;2010:687067. doi: 10.1155/2010/687067. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Cardiovasc Psychiatry Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20862385 Free PMC article.
-
S100B actions on glial and neuronal cells in the developing brain: an overview.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jul 4;18:1425525. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1425525. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39027325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reliability of S100B in predicting severity of central nervous system injury.Neurocrit Care. 2007;6(2):121-38. doi: 10.1007/s12028-007-0008-x. Neurocrit Care. 2007. PMID: 17522796 Review.
-
The calcium-binding protein S100B down-regulates p53 and apoptosis in malignant melanoma.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 27;285(35):27487-27498. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.155382. Epub 2010 Jun 29. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20587415 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between contact inhibition and intranuclear S100C of normal human fibroblasts.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jun 12;149(6):1193-206. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.6.1193. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10851017 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allore R, O’Hanlon D, Price R, Neilson K, Willard H F, Cox D R, Marks A, Dunn R J. Gene encoding the β-subunit of S100 protein is on chromosome 21: implication for Down syndrome. Science. 1988;239:1311–1313. - PubMed
-
- Artuso M, Esteve A, Brésil H, Vuillaume M, Hall J. The role of the Ataxia telangiectasia gene in the p53, WAF1/CIP1 (p21) and GADD45-mediated response to DNA damage produced by ionising radiation. Oncogene. 1995;11:1427–1435. - PubMed
-
- Asai A, Miyagi Y, Sugiyama A, Gamanuma M, Hong S I, Takamoto S, Nomura K, Matsutani M, Takakura K, Kuchino Y. Negative effects of wild-type p53 and s-Myc on cellular growth and tumorigenicity of glioma cells. J Neuro-Oncol. 1994;19:259–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
