CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha is a regulatory switch sufficient for induction of granulocytic development from bipotential myeloid progenitors
- PMID: 9632814
- PMCID: PMC109014
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4301
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha is a regulatory switch sufficient for induction of granulocytic development from bipotential myeloid progenitors
Abstract
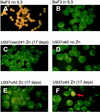
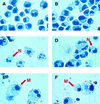
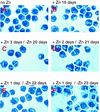
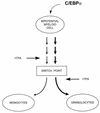
The transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) regulates a number of myeloid cell-specific genes. To delineate the role of C/EBPalpha in human granulopoiesis, we studied its expression and function in human primary cells and bipotential (granulocytic/monocytic) myeloid cell lines. We show that the expression of C/EBPalpha initiates with the commitment of multipotential precursors to the myeloid lineage, is specifically upregulated during granulocytic differentiation, and is rapidly downregulated during the alternative monocytic pathway. Conditional expression of C/EBPalpha alone in stably transfected bipotential cells triggers neutrophilic differentiation, concomitant with upregulation of the granulocyte-specific granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor and secondary granule protein genes. Moreover, induced expression of C/EBPalpha in bipotential precursors blocks their monocytic differentiation program. These results indicate that C/EBPalpha serves as a myeloid differentiation switch acting on bipotential precursors and directing them to mature to granulocytes.
Figures



References
-
- Ahuja S K, Shetty A, Tiffany H L, Murphy P M. Comparison of the genomic organization and promoter function for human interleukin-8 receptors A and B. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:26381–26389. - PubMed
-
- Andrews R G, Bryant E M, Bartelmez S H, Muirhead D Y, Knitter G H, Bensinger W, Strong D M, Bernstein I D. CD34+ marrow cells, devoid of T and B lymphocytes, reconstitute stable lymphopoiesis and myelopoiesis in lethally irradiated allogeneic baboons. Blood. 1992;80:1693–1701. - PubMed
-
- Antonson P, Stellan B, Yamanaka R, Xanthopoulos K G. A novel human CCAAT/enhancer binding protein gene, C/EBPɛ, is expressed in cells of lymphoid and myeloid lineages and is localized on chromosome 14q11.2 close to the T-cell receptor α/δ locus. Genomics. 1996;35:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Antonson P, Xanthopoulos K G. Molecular cloning, sequence, and expression patterns of the human gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995;215:106–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
