Interactions among Drosophila nuclear envelope proteins lamin, otefin, and YA
- PMID: 9632815
- PMCID: PMC109015
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4315
Interactions among Drosophila nuclear envelope proteins lamin, otefin, and YA
Abstract
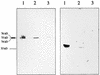
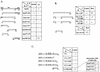
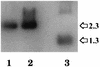
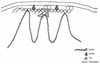
The nuclear envelope plays many roles, including organizing nuclear structure and regulating nuclear events. Molecular associations of nuclear envelope proteins may contribute to the implementation of these functions. Lamin, otefin, and YA are the three Drosophila nuclear envelope proteins known in early embryos. We used the yeast two-hybrid system to explore the interactions between pairs of these proteins. The ubiquitous major lamina protein, lamin Dm, interacts with both otefin, a peripheral protein of the inner nuclear membrane, and YA, an essential, developmentally regulated protein of the nuclear lamina. In agreement with this interaction, lamin and otefin can be coimmunoprecipitated from the vesicle fraction of Drosophila embryos and colocalize in nuclear envelopes of Drosophila larval salivary gland nuclei. The two-hybrid system was further used to map the domains of interaction among lamin, otefin, and YA. Lamin's rod domain interacts with the complete otefin protein, with otefin's hydrophilic NH2-terminal domain, and with two different fragments derived from this domain. Analogous probing of the interaction between lamin and YA showed that the lamin rod and tail plus part of its head domain are needed for interaction with full-length YA in the two-hybrid system. YA's COOH-terminal region is necessary and sufficient for interaction with lamin. Our results suggest that interactions with lamin might mediate or stabilize the localization of otefin and YA in the nuclear lamina. They also suggest that the need for both otefin and lamin in mediating association of vesicles with chromatin might reflect the function of a protein complex that includes these two proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A hydrophilic lamin-binding domain from the Drosophila YA protein can target proteins to the nuclear envelope.J Cell Sci. 2003 May 15;116(Pt 10):2067-72. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00402. Epub 2003 Apr 1. J Cell Sci. 2003. PMID: 12679383
-
Localization and posttranslational modifications of otefin, a protein required for vesicle attachment to chromatin, during Drosophila melanogaster development.Mol Cell Biol. 1997 Jul;17(7):4114-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.17.7.4114. Mol Cell Biol. 1997. PMID: 9199347 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of the male pronuclear lamina in Drosophila melanogaster.Dev Biol. 1997 Apr 15;184(2):187-96. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1997.8523. Dev Biol. 1997. PMID: 9133429
-
Lamins and lamin-binding proteins in functional chromatin organization.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1999;9(3-4):257-65. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v9.i3-4.100. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1999. PMID: 10651242 Review.
-
LEM-Domain proteins: new insights into lamin-interacting proteins.Int Rev Cytol. 2007;261:1-46. doi: 10.1016/S0074-7696(07)61001-8. Int Rev Cytol. 2007. PMID: 17560279 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for nuclear lamins in nuclear envelope assembly.J Cell Biol. 2001 Jul 9;154(1):61-70. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200101025. J Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11448990 Free PMC article.
-
LAP2 binds to BAF.DNA complexes: requirement for the LEM domain and modulation by variable regions.EMBO J. 2001 Apr 2;20(7):1754-64. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.7.1754. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11285238 Free PMC article.
-
Lamin C and chromatin organization in Drosophila.J Genet. 2010 Apr;89(1):37-49. doi: 10.1007/s12041-010-0009-y. J Genet. 2010. PMID: 20505245
-
Laminopathies: what can humans learn from fruit flies.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018 Jul 6;23:32. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0093-1. eCollection 2018. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30002683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional analysis of centrosomal kinase substrates in Drosophila melanogaster reveals a new function of the nuclear envelope component otefin in cell cycle progression.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;32(17):3554-69. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00814-12. Epub 2012 Jul 2. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22751930 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashery-Padan R, Weiss A M, Feinstein N, Gruenbaum Y. Distinct regions specify the targeting of otefin to the nucleoplasmic side of the nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:2493–2499. - PubMed
-
- Ashery-Padan, R., and Y. Gruenbaum. Unpublished observations.
-
- Ausubel F M, Brent R, Kingston R E, Moore D D, Seidman J G, Smith J A, Struhl K. Current protocols in molecular biology. New York, N.Y: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 1994.
-
- Baricheva E A, Berrios M, Bogachev S S, Borisevich I V, Lapik E R, Sharakhov I V, Stuurman N, Fisher P A. DNA from Drosophila melanogaster beta-heterochromatin binds specifically to nuclear lamins in vitro and the nuclear envelope in situ. Gene. 1996;171:171–176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
