PEX12, the pathogenic gene of group III Zellweger syndrome: cDNA cloning by functional complementation on a CHO cell mutant, patient analysis, and characterization of PEX12p
- PMID: 9632816
- PMCID: PMC109016
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.18.7.4324
PEX12, the pathogenic gene of group III Zellweger syndrome: cDNA cloning by functional complementation on a CHO cell mutant, patient analysis, and characterization of PEX12p
Abstract
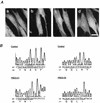
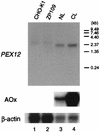
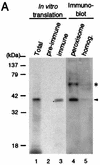
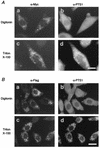
Rat PEX12 cDNA was isolated by functional complementation of peroxisome deficiency of a mutant CHO cell line, ZP109 (K. Okumoto, A. Bogaki, K. Tateishi, T. Tsukamoto, T. Osumi, N. Shimozawa, Y. Suzuki, T. Orii, and Y. Fujiki, Exp. Cell Res. 233:11-20, 1997), using a transient transfection assay and an ectopic, readily visible marker, green fluorescent protein. This cDNA encodes a 359-amino-acid membrane protein of peroxisomes with two transmembrane segments and a cysteine-rich zinc finger, the RING motif. A stable transformant of ZP109 with the PEX12 was morphologically and biochemically restored for peroxisome biogenesis. Pex12p was shown by expression of bona fide as well as epitope-tagged Pex12p to expose both N- and C-terminal regions to the cytosol. Fibroblasts derived from patients with the peroxisome deficiency Zellweger syndrome of complementation group III (CG-III) were also complemented for peroxisome biogenesis with PEX12. Two unrelated patients of this group manifesting peroxisome deficiency disorders possessed homozygous, inactivating PEX12 mutations: in one, Arg180Thr by one point mutation, and in the other, deletion of two nucleotides in codons for 291Asn and 292Ser, creating an apparently unchanged codon for Asn and a codon 292 for termination. These results indicate that the gene encoding peroxisome assembly factor Pex12p is a pathogenic gene of CG-III peroxisome deficiency. Moreover, truncation and site mutation studies, including patient PEX12 analysis, demonstrated that the cytoplasmically oriented N- and C-terminal parts of Pex12p are essential for biological function.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Human PEX19: cDNA cloning by functional complementation, mutation analysis in a patient with Zellweger syndrome, and potential role in peroxisomal membrane assembly.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 Mar 2;96(5):2116-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.5.2116. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10051604 Free PMC article.
-
Human PEX1 cloned by functional complementation on a CHO cell mutant is responsible for peroxisome-deficient Zellweger syndrome of complementation group I.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Apr 14;95(8):4350-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.8.4350. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9539740 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in PEX10 is the cause of Zellweger peroxisome deficiency syndrome of complementation group B.Hum Mol Genet. 1998 Sep;7(9):1399-405. doi: 10.1093/hmg/7.9.1399. Hum Mol Genet. 1998. PMID: 9700193
-
[Human peroxisome-deficient disorders and pathogenic gene].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1994 Dec;34(12):1219-21. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1994. PMID: 7539728 Review. Japanese.
-
[Molecular biology of peroxisome biogenesis].Nihon Rinsho. 1993 Sep;51(9):2336-42. Nihon Rinsho. 1993. PMID: 8411711 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Mild reduction of plasmalogens causes rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata: functional characterization of a novel mutation.J Hum Genet. 2014 Jul;59(7):387-92. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2014.39. Epub 2014 May 22. J Hum Genet. 2014. PMID: 24849933
-
Hsp70 regulates the interaction between the peroxisome targeting signal type 1 (PTS1)-receptor Pex5p and PTS1.Biochem J. 2001 Jul 1;357(Pt 1):157-65. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3570157. Biochem J. 2001. PMID: 11415446 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome sequencing in patients with inherited neuropathies: outcome and challenges.J Neurol. 2014 May;261(5):970-82. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7289-8. Epub 2014 Mar 15. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24627108
-
Characterization of glycosomal RING finger proteins of trypanosomatids.Exp Parasitol. 2007 May;116(1):14-24. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2006.11.004. Epub 2006 Dec 26. Exp Parasitol. 2007. PMID: 17188680 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotype-genotype relationships in complementation group 3 of the peroxisome-biogenesis disorders.Am J Hum Genet. 1998 Nov;63(5):1294-306. doi: 10.1086/302103. Am J Hum Genet. 1998. PMID: 9792857 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berteaux-Lecellier V, Picard M, Thompson-Coffe C, Zickler D, Panvier-Adoutte A, Simonet J-M. A nonmammalian homolog of the PAF1 gene (Zellweger syndrome) discovered as a gene involved in caryogamy in the fungus Podospora anserina. Cell. 1995;81:1043–1051. - PubMed
-
- Braverman N, Steel G, Obie C, Moser A, Moser H, Gould S J, Valle D. Human PEX7 encodes the peroxisomal PTS2 receptor and is responsible for rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata. Nat Genet. 1997;15:369–376. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward W W, Prasher D C. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science (Washington, DC) 1994;263:802–805. - PubMed
-
- Chang C-C, Lee W-H, Moser H, Valle D, Gould S J. Isolation of the human PEX12 gene, mutated in group 3 of the peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat Genet. 1997;15:385–388. - PubMed
-
- Chomczynski P, Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-PhOH-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987;162:156–159. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
