His...Asp catalytic dyad of ribonuclease A: structure and function of the wild-type, D121N, and D121A enzymes
- PMID: 9636030
- PMCID: PMC2849997
- DOI: 10.1021/bi972766q
His...Asp catalytic dyad of ribonuclease A: structure and function of the wild-type, D121N, and D121A enzymes
Abstract
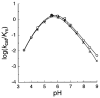
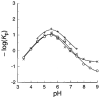
The side chains of histidine and aspartate residues form a hydrogen bond in the active sites of many enzymes. In serine proteases, the His...Asp hydrogen bond of the catalytic triad is known to contribute greatly to catalysis, perhaps via the formation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond. In bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A (RNase A), the His...Asp dyad is composed of His119 and Asp121. Previously, site-directed mutagenesis was used to show that His119 has a fundamental role, to act as an acid during catalysis of RNA cleavage [Thompson, J. E., and Raines, R. T. (1994) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116, 5467-5468]. Here, Asp121 was replaced with an asparagine or alanine residue. The crystalline structures of the two variants were determined by X-ray diffraction analysis to a resolution of 1.6 A with an R-factor of 0.18. Replacing Asp121 with an asparagine or alanine residue does not perturb the overall conformation of the enzyme. In the structure of D121N RNase A, Ndelta rather than Odelta of Asn121 faces His119. This alignment in the crystalline state is unlikely to exist in solution because catalysis by the D121N variant is not compromised severely. The steady-state kinetic parameters for catalysis by the wild-type and variant enzymes were determined for the cleavage of uridylyl(3'-->5')adenosine and poly(cytidylic acid), and for the hydrolysis of uridine 2',3'-cyclic phosphate. Replacing Asp121 decreases the values of kcat/Km and kcat for cleavage by 10-fold (D121N) and 10(2)-fold (D121A). Replacing Asp121 also decreases the values of kcat/Km and kcat for hydrolysis by 10(0. 5)-fold (D121N) and 10-fold (D121A) but has no other effect on the pH-rate profiles for hydrolysis. There is no evidence for the formation of a low-barrier hydrogen bond between His119 and either an aspartate or an asparagine residue at position 121. Apparently, the major role of Asp121 is to orient the proper tautomer of His119 for catalysis. Thus, the mere presence of a His...Asp dyad in an enzymic active site is not a mandate for its being crucial in effecting catalysis.
Figures




References
-
- Neurath H. In: Proteolytic Enzymes: A Practical Approach. Beynon RJ, Bond JS, editors. IRL Press; New York: 1989. pp. 1–13.
-
- Blow DM, Birktoft JJ, Hartley BS. Nature. 1969;221:337–340. - PubMed
-
- Blow DM. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1997;22:405–408. - PubMed
-
- Neurath H. Science. 1984;224:350–357. - PubMed
-
- Brady L, Brzozowski AM, Derewenda ZS, Dodson E, Dodson G, Tolley S, Turkenburg JH, Christiansen L, Huge-Jensen B, Norskov L, L. T, Menge U. Nature. 1990;343:767–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

