Su(UR)ES: a gene suppressing DNA underreplication in intercalary and pericentric heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes
- PMID: 9636184
- PMCID: PMC22673
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7532
Su(UR)ES: a gene suppressing DNA underreplication in intercalary and pericentric heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes
Abstract
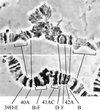
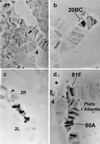
A genetic locus suppressing DNA underreplication in intercalary heterochromatin (IH) and pericentric heterochromatin (PH) of the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster salivary glands, has been described. Found in the In(1)scV2 strain, the mutation, designated as Su(UR)ES, was located on chromosome 3L at position 34. 8 and cytologically mapped to region 68A3-B4. A cytological phenotype was observed in the salivary gland chromosomes of larvae homozygous and hemizygous for Su(UR)ES: (i) in the IH regions, that normally are incompletely polytenized and so they often break to form "weak points," underreplication is suppressed, breaks and ectopic contacts disappear; (ii) the degree of polytenization in PH grows higher. That is why the regions in chromosome arm basements, normally beta-heterochromatic, acquire a distinct banding pattern, i. e., become euchromatic by morphological criteria; (iii) an additional bulk of polytenized material arises between the arms of chromosome 3 to form a fragment with a typical banding pattern. Chromosome 2 PH reveals additional alpha-heterochromatin. Su(UR)ES does not affect the viability, fertility, or morphological characters of the imago, and has semidominant expression in the heterozygote and distinct maternal effect. The results obtained provide evidence that the processes leading to DNA underreplication in IH and PH are affected by the same genetic mechanism.
Figures



References
-
- Heitz E. Planta. 1932;28:571–630.
-
- Lohe A R, Hilliker A J. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1995;5:746–755. - PubMed
-
- Eissenberg J C, Elgin S C R, Paro R. In: Chromatine Structure and Gene Expression. Elgin S C R, editor. Oxford: IRL; 1995. pp. 147–171.
-
- Henikoff S. In: Gene Silencing in Higher Plants and Related Phenomena in Other Eukaryotes. Meyer P, editor. Berlin: Springer; 1995. pp. 193–208.
-
- Elgin S C R. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1996;6:193–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

