Resistance to endotoxic shock and reduced neutrophil migration in mice deficient for the Src-family kinases Hck and Fgr
- PMID: 9636192
- PMCID: PMC22689
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.95.13.7580
Resistance to endotoxic shock and reduced neutrophil migration in mice deficient for the Src-family kinases Hck and Fgr
Abstract
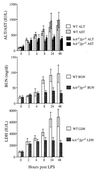
Signal transduction through the leukocyte integrins is required for the processes of firm adhesion, activation, and chemotaxis of neutrophils during inflammatory reactions. Neutrophils isolated from knockout mice that are deficient in the expression of p59/61(hck) (Hck) and p58(c-fgr) (Fgr), members of the Src-family of protein tyrosine kinases, have been shown to be defective in adhesion mediated activation. Cells from these animals have impaired induction of respiratory burst and granule secretion following plating on surfaces that crosslink beta2 and beta3 integrins. To determine if the defective function of hck-/-fgr-/- neutrophils observed in vitro also results in impaired inflammatory responses in vivo, we examined responses induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection in these animals. The hck-/-fgr-/- mice showed marked resistance to the lethal effects of high-dose LPS injection despite the fact that high levels of serum tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1alpha were detected. Serum chemistry analysis revealed a marked reduction in liver and renal damage in mutant mice treated with LPS, whereas blood counts showed a marked neutrophilia that was not seen in wild-type animals. Direct examination of liver sections from mutant mice revealed reduced neutrophil migration into the tissue. These data demonstrate that defective integrin signaling in neutrophils, caused by loss of Hck and Fgr tyrosine kinase activity, results in impaired inflammation-dependent tissue injury in vivo.
Figures


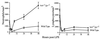

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

