C/EBPbeta, but not C/EBPalpha, is essential for ductal morphogenesis, lobuloalveolar proliferation, and functional differentiation in the mouse mammary gland
- PMID: 9637692
- PMCID: PMC316914
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.12.12.1917
C/EBPbeta, but not C/EBPalpha, is essential for ductal morphogenesis, lobuloalveolar proliferation, and functional differentiation in the mouse mammary gland
Abstract
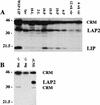
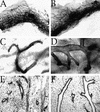
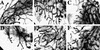
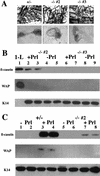
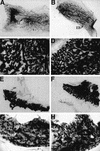
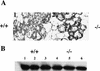
The CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins (C/EBPs) are differentially expressed throughout mammary gland development and interact with binding sites within the promoter of a milk protein gene, beta-casein. The specific roles of C/EBPbeta and C/EBPalpha in mouse mammary gland development and differentiation have been investigated in mice that carry targeted deletions of these genes. C/EBPbeta-/- virgin mice exhibited cystic, enlarged mammary ducts with decreased secondary branching. Transplantation of C/EBPbeta-/- mammary epithelium into the cleared mammary fat pads of nude mice confirmed that this defect in ductal morphogenesis was intrinsic to the epithelium. When treated with estrogen/progesterone (E+P) to simulate pregnancy, C/EBPbeta-/- mammary glands displayed only limited lobuloalveolar development and ductal side branching. Primary mammary epithelial cells obtained from E+P-treated C/EBPbeta-/- mice that were cultured on extracellular matrix gels did not functionally differentiate in response to lactogenic hormones despite their organization into three-dimensional structures. Expression of beta-casein protein was inhibited 85%-100% and whey acidic protein (WAP) was undetectable. In contrast, no detectable alterations in mammary development or beta-casein expression were observed in mammary outgrowths derived from newborn C/EBPalpha-/- mammary epithelium transplanted into the cleared mammary fat pads of syngeneic hosts. These results demonstrate that C/EBPbeta, but not C/EBPalpha, is required for ductal morphogenesis, lobuloalveolar development, and functional differentiation of mammary epithelial cells.
Figures
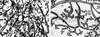

Similar articles
-
The C/EBPbeta transcription factor regulates epithelial cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammary gland.Genes Dev. 1998 Jun 15;12(12):1907-16. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.12.1907. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9637691 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of steroid and prolactin receptor patterning in the mammary gland correlates with a block in lobuloalveolar development.Mol Endocrinol. 2002 Dec;16(12):2675-91. doi: 10.1210/me.2002-0239. Mol Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 12456789
-
Expression and function of CCAAT/enhancer binding proteinbeta (C/EBPbeta) LAP and LIP isoforms in mouse mammary gland, tumors and cultured mammary epithelial cells.J Cell Biochem. 2001;82(3):357-70. doi: 10.1002/jcb.1167. J Cell Biochem. 2001. PMID: 11500913
-
The role of C/EBPbeta in mammary gland development and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003 Apr;8(2):191-204. doi: 10.1023/a:1025900908026. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2003. PMID: 14635794 Review.
-
Delivering the message: epimorphin and mammary epithelial morphogenesis.Trends Cell Biol. 2003 Aug;13(8):426-34. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(03)00146-6. Trends Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 12888295 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding protein β is dispensable for development of lung adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 13;10(3):e0120647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120647. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25767874 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins in normal mammary development and breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2002;4(3):113-21. doi: 10.1186/bcr428. Epub 2002 Apr 19. Breast Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12052253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging functions of C/EBPβ in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 25;13:1111522. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1111522. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36761942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
c-Myc affects mRNA translation, cell proliferation and progenitor cell function in the mammary gland.BMC Biol. 2009 Sep 28;7:63. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-7-63. BMC Biol. 2009. PMID: 19785743 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation.Biochem J. 2002 Aug 1;365(Pt 3):561-75. doi: 10.1042/BJ20020508. Biochem J. 2002. PMID: 12006103 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alam T, An MR, Papaconstantinou J. Differential expression of three C/EBP isoforms in multiple tissues during the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:5021–5024. - PubMed
-
- Bissell MJ, Aggeler J. Dynamic reciprocity: How do extracellular matrix and hormones direct gene expression? Prog Clin Biol Res. 1987;249:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Blais S, Boudreau F, Beaulieu JF, Asselin C. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein isoforms expression in the colon of neonatal mice. Dev Dyn. 1995;204:66–76. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes & Dev. 1991;5:1538–1552. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
